Figure 4.
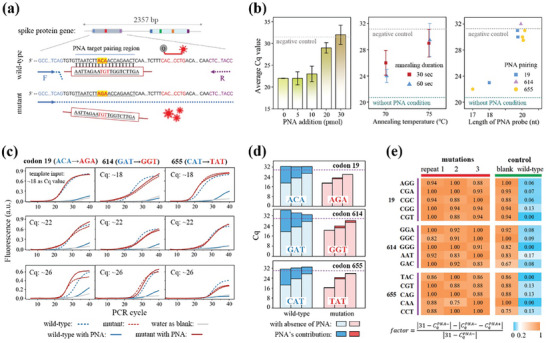
Principle and specificity of PNA design to distinguish SNPs at codon 19, 614, and 655 of the spike protein gene. a) Design of the PNA‐assisted assay for detection of point mutation at codon 19. A PNA sequence was introduced to block the amplification of wild‐type allele, and a TaqMan assay was included as amplification reporter. b) PNA clamping effect on wild‐type DNA as functions of loading amount, annealing temperature and duration, and sequence length. mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3). c) qPCR fluorescence was measured at three codons with different DNA inputs indicating that PNA clamps blocked wild‐type templates amplification while had negligible impact on mutant templates. d) Apparently different contributions of PNA on wild‐type and mutant templates amplification across those samples. The blank level indicated by the dotted lines represented the mean + twofold of the s.e.m. from three negative control tests without DNA input. e) Heatmap showing PNA‐assisted qPCR enabled the identification of 15 other possible mutations corresponding to the T19R, O614G, and H655Y codon changes. A factor is defined to describe the relative effect of PNA on the testing samples, where the value of 31 in the equation stands for the Cq of negative control.
