Figure 1.
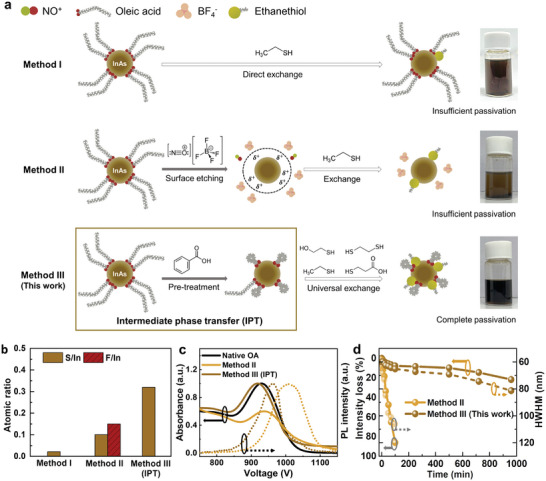
Surface modification of InAs colloidal quantum dots (CQDs) using the intermediate phase transfer (IPT) method. a) Schematics of three ligand exchange methods using InAs CQD and the corresponding photographic images of the resultant CQD ink: i) direct ligand exchange method, ii) surface etching method using NOBF4, and iii) IPT. All photographs exhibit the ethanethiol (ET)‐capped CQD ink dissolved in 2‐methylanisole (2‐MA). b) X‐ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) atomic ratios (ratios of sulfur to indium (brown) and fluorine to indium (red)) of thiol‐exchanged CQD surfaces using various ligand exchange methods. c) Normalized absorbance (solid line) and PL (dashed line) spectra of CQD inks fabricated by methods II (yellow‐brown) and method III (brown), compared to the absorbance spectrum of native OA ligands (black, solid). d) Intensity loss (line) and HWHM (dashed) were measured using the absorbance spectra as a function of time for the CQD inks obtained using methods II (yellow‐brown) and III (brown).
