Fig.3: QC6352 causes impaired ribosome biogenesis in WiT49 and HEK293 cells.
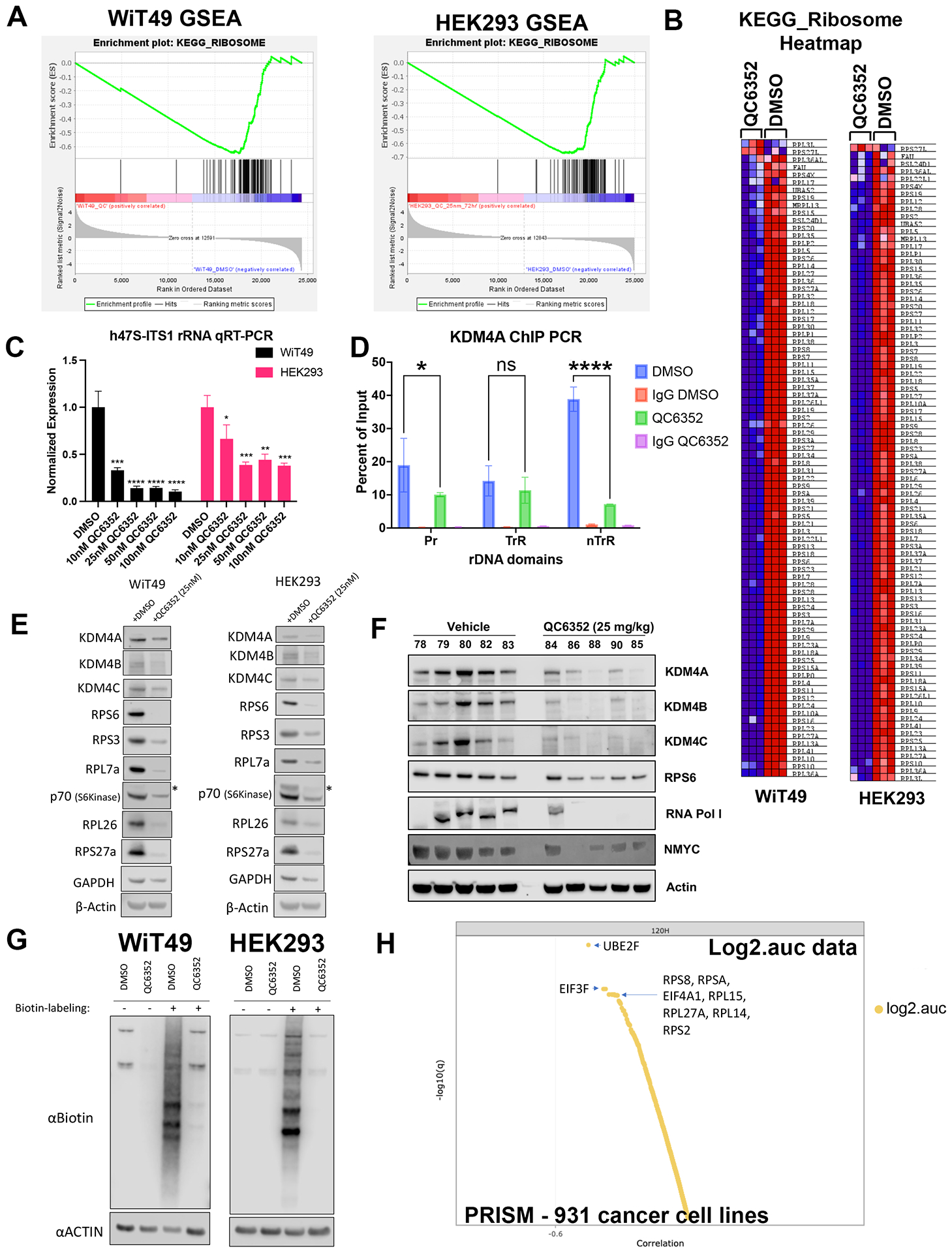
RNA-seq was performed on WiT49 and HEK293 cells treated with 25 nM QC6352 for 72 hours. (A) Gene set enrichment analysis demonstrated the KEGG_RIBOSOME pathway to be significantly downregulated in both WiT49 and HEK293 cells. (B) Heatmap display of the KEGG_RIBOSOME pathway gene set demonstrates marked reduction of ribosomal protein gene expression with QC6352 treatment in HEK293 and WiT49. (C) qRT-PCR for human 47S rRNA demonstrates a dose-dependent reduction of ribosomal RNA transcription with QC6352 treatment for 72 hours in WiT49 and HEK293 cells (t-test p values *<0.05, **<0.01, ***<0.001, ****<0.0001). (D)25nM QC6352 treatment for 72 hours resulted in decreased KDM4A occupancy at the human rDNA promoter region (Pr) and nontranscribed regions (nTrR), but not the transcribed regions (TrR) in WiT49 cells as assessed by KDM4A ChIP PCR. (E) Western blot shows downregulation of KDM4A, KDM4B, KDM4C, the ribosomal proteins RPS6, RPS3, RPL7a, RPL26, and RPS27a, and P70S6 kinase in response to QC6352 treatment. (F) HEK293 xenograft tumors harvested at the completion of QC6352 treatment (25 mg/kg oral gavage for three weeks) demonstrate a reduction in KDM4A, KDM4B, KDM4C, ribosomal protein S6, RNA polymerase I, and N-MYC by western blot compared to vehicle control. (G) Click-iT metabolic labeling of nascent protein synthesis demonstrated blockade of new protein synthesis in response to QC6352 treatment in WiT49 and HEK293 cells. (H) PRISM multiplexed cell line profiling RNA expression and compound sensitivity correlation analysis data from 931 cancer cell lines demonstrated that six of the top ten genes with basal expression that correlated to QC6352 sensitivity were ribosomal genes: RPS8, RPSA, RPL15, RPL27A, RPL14, and RPS and two of the top 10 genes were translational elongation factors: EIF3F and EIF4A1. The top “hit” was the ubiquitination-associated NEDD8-conjugating enzyme UBE2F.
