Fig.5: The QC6352 treatment phenotype is mirrored by knockdown of KDM4A.
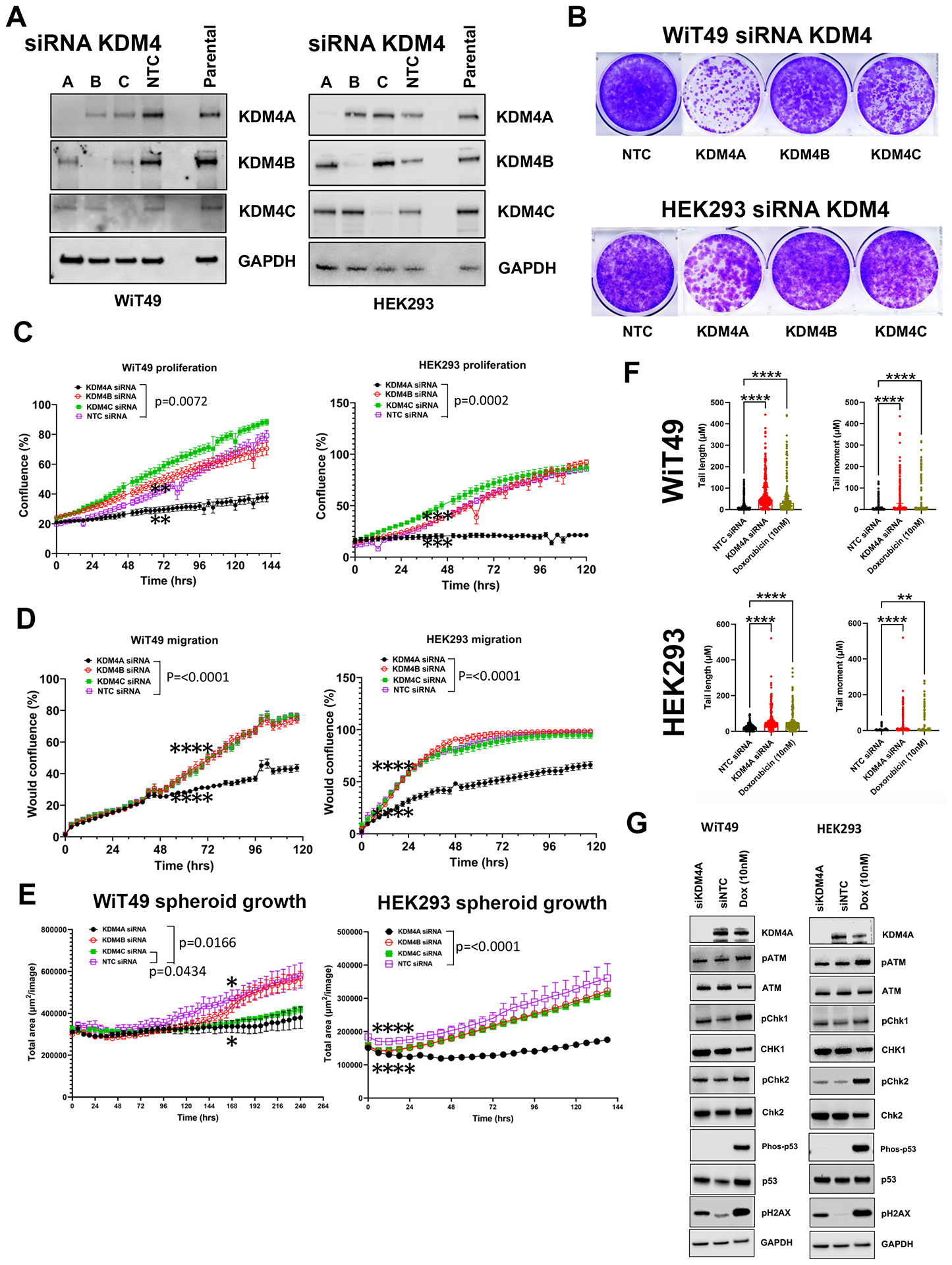
(A) Western blot confirmed siRNA-mediated knockdown of KDM4A, KDM4B, KDM4C and non-targeting control (NTC) in WiT49 and HEK293 (10nM siRNAs). (B) Crystal Violet assay demonstrated that KDM4A knockdown caused reduced proliferation in WiT49 and HEK293. KDM4C knockdown also caused reduced proliferation in WiT49. KDM4A knockdown caused reduced proliferation (C) and migration (D) compared to KDM4B, KDM4C, and NTC siRNA in both WiT49 and HEK293 by live-cell microscopy. (E) Spheroid growth was reduced by KDM4A knockdown in WiT49 and HEK293. (F) SiKDM4A induces DNA damage detected by the Comet assay. Doxorubicin-treated cells (10nM for 72 hours) are included as positive control. Kruskal-Wallis p-values are shown. (G) Western blot corroborates DNA damage caused by siKDM4A marked by increased detection of pH2AX in WiT49 and HEK293. A DNA damage checkpoint protein response does not appear to be induced by siKDM4A. For C-E, the rightmost asterix indicates timepoint at which separation in curves is statistically significant (paired two-tailed t-test p<0.05) and persists throughout remaining indicated duration.
