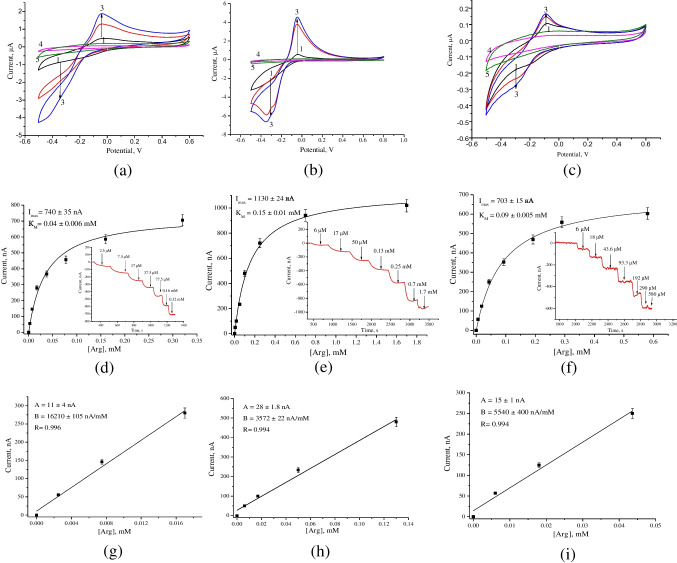
Fig. 4.
Electrochemical characteristics of GCEs modified with nCu and ArgO (a, d, g), ADI (b, e, h), and ARG/urease (c, f, i) in the presence of increased concentrations of Arg. CVs (a–c) under injected Arg up to concentrations 0.2 mM (2), 0.5 mM (3) in comparison with nCdCu/GCE (1) and unmodified GCE (4), and enzyme/GCEs (5) (as a control electrodes) in the presence of 0.5 mM Arg; amperometric responses (d–f) and calibration curves (g–i) of peak current vs total Arg concentration. Conditions: CV scan rate 5 mV·s−1 vs. Ag/AgCl, pH 7.5 (for ADI- or ArgO-based sensor) or 50 mM TB, pH 8 (for ARG/urease sensor); working potential for all bioelectrodes was ArgOx/nCdCu/GCE, ARG/urease/nCdCu/GCE and ADI/nCdCu/GCE was – 300 mV