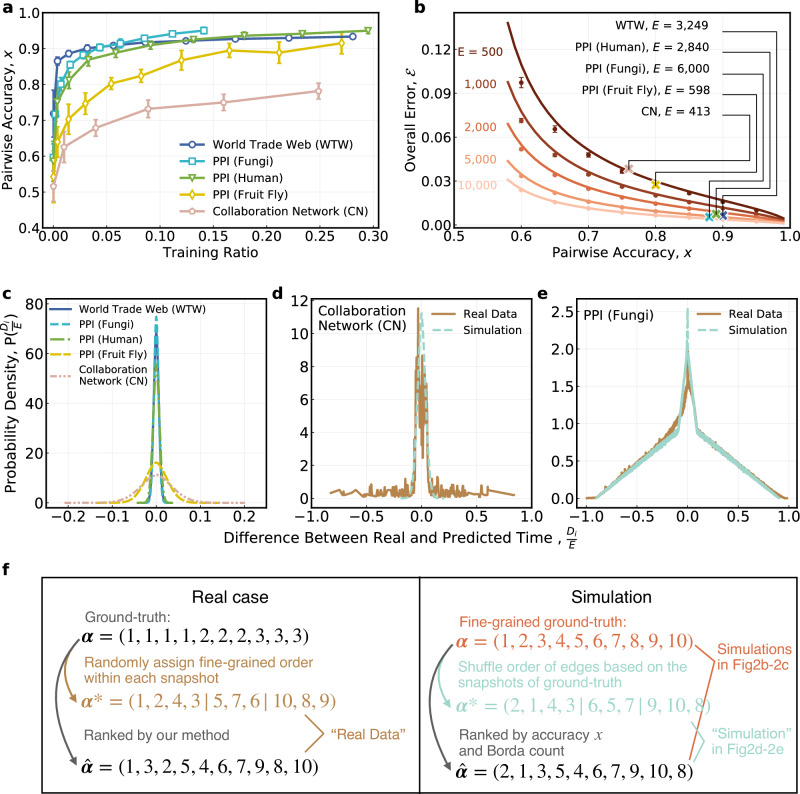
Fig. 2. Performance of the ensemble model and the restored edge sequence.
a Test accuracy of the ensemble model as a function of the percentage of edge pairs used for training. Each data point with error bars marks the corresponding simulation results (average ± standard deviation of 100 simulations), the same for b. b Overall error as a function of the accuracy x of the ensemble model for different numbers of edges E. The solid curves represent the theoretical results from Eq. (2) and the colored crosses stand for the simulation results using the E and x of five real-world networks. c Simulated distributions of Di/E using the E and x of five real-world networks. Specifically, assuming the ground-truth sequence α = (1, 2, …, E), 100(1 − x)% of all edge pairs are randomly selected and artificially assigned the wrong generation order while the remaining edge pairs are assigned the correct one. Then, the restored edge sequence is obtained by applying the ranking algorithm on the artificially predicted order of all edge pairs and Di’s are calculated accordingly. d, e Comparisons between the real and simulated distributions of Di/E based on the collaboration network (CN) and the PPI network (Fungi). f Diagram illustrating how the distributions in c–e are obtained. The left and right panels show the calculation of Di under a real case when we only know the coarse-grained ground-truth sequence and a simulation when we know the fine-grained ground-truth sequence, respectively. For the real case, Di cannot be calculated directly as so the idea is to consider an intermediate sequence α* by randomly assigning fine-grained order to edges added within the same snapshot and Di is calculated as instead. Then the distribution of Di/E is obtained by averaging over 5000 α*’s to take the randomness into account. For the simulation, the calculation of Di follows a similar procedure to match with the real case. The results under the real case and simulation are labeled as “Real Data” and “Simulation” in d and e. See Algorithms 2-3 in the Methods section for more details.