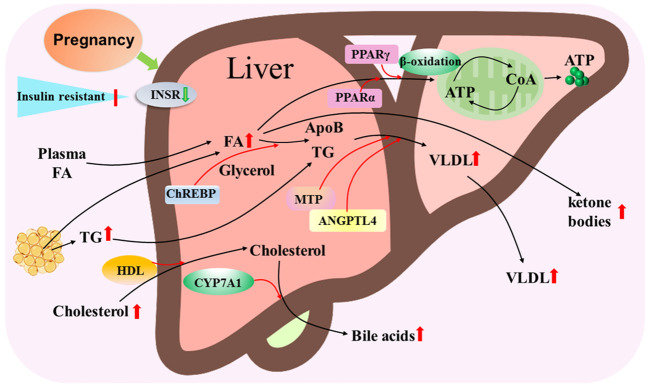
Figure 4.
Hepatic lipid metabolic pathway during pregnancy. Pregnancy leads to insulin resistance and downregulation of insulin receptor (INSR), and increases in transport of fatty acids (FAs) from plasma and adipose tissue, triglyceride (TG) and cholesterol that are transported by high-density lipoproteins (HDL) particles to the liver. Carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein (ChREBP) is involved in triglyceride synthesis from FAs and glycerol, and peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha (PPARα) and PPARγ regulate the β-oxidation of FA to release ATP through tricarboxylic acid cycle. Microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) and angiopoietin like 4 (ANGPTL4) modulate VLDL assembly by apolipoprotein B (ApoB) and TG, which result in an increase in VLDL release from the liver. In addition, cytochrome P450 family 7 subfamily A member 1 (CYP7A1) converts cholesterol to bile acids that are released from the liver to improve the digestion and absorption of lipids. Moreover, some free FAs are oxidized as ketone bodies that are released from the liver.