Figure 6. Symbiotic mechanism of S. epidermidis-mediated pathogen exclusion on the nasal epithelium – in vivo tests.
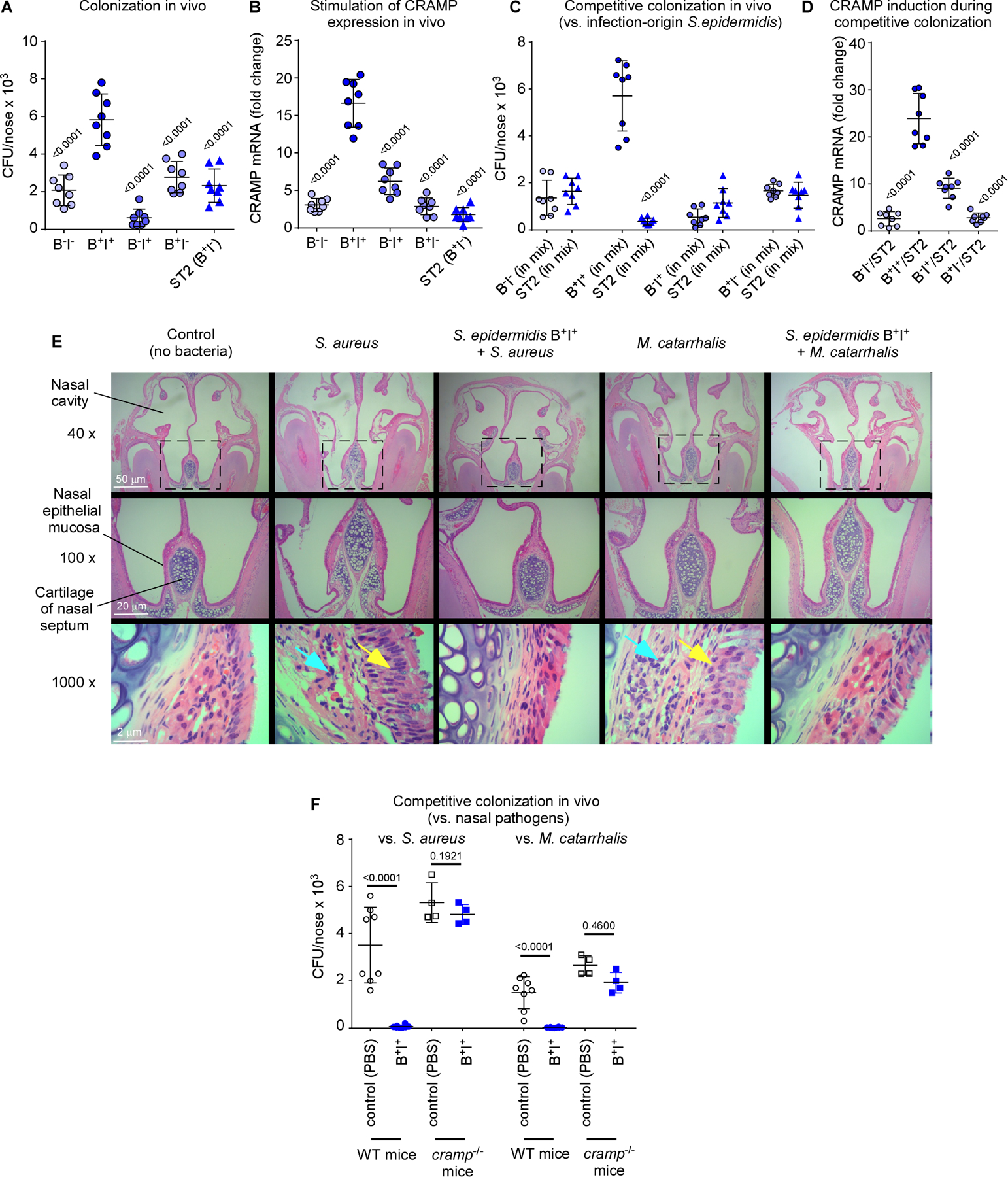
(A) Nasal colonization in mice of selected S. epidermidis commensal strains (B−I−, weak biofilm former and low AMP induction capacity; B+I+, strong biofilm former and high AMP induction capacity; B−I+, weak biofilm former and high AMP induction capacity; B+I−, strong biofilm-former and low AMP induction capacity, see Table S2), and an infection-origin isolate with the B+I− phenotype characteristic for that group. Inocula, 1 × 107 CFU, once a day for 4 days, CFU determination 6 days after first instilment. (B) Induction of cramp gene in the same experiment as in panel A. (C) Competitive nasal colonization with the four selected commensal S. epidermidis strains and the infection-origin ST2 strain (1:1 inocula, 1 × 107 CFU each, instilments and CFU determination as described for panel A). (D) Induction of cramp gene in the same experiment as in panel C. (E,F) Competitive nasal colonization with B+I+ S. epidermidis and S. aureus or M. catarrhalis (S. epidermidis, 1 × 107 CFU every day over four days; S. aureus, 1 × 108 CFU at day 6; M. catarrhalis, 4 × 109 CFU at day 6). (E) Histological examination of noses. Yellow arrows, proliferation of cilia in nasal epithelial mucosa; blue arrows, destruction of epithelial submucosa. (F) CFU. (A-D, F) n=8. (B,D) Three measurements were taken for determination of CRAMP mRNA expression. The shown data represent the average for every mouse. (A,B,D) Statistical analysis is by 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-tests versus data obtained with with B+I+. (C,F) Statistical analysis is by unpaired t-tests. Error bars show means ± SD.
