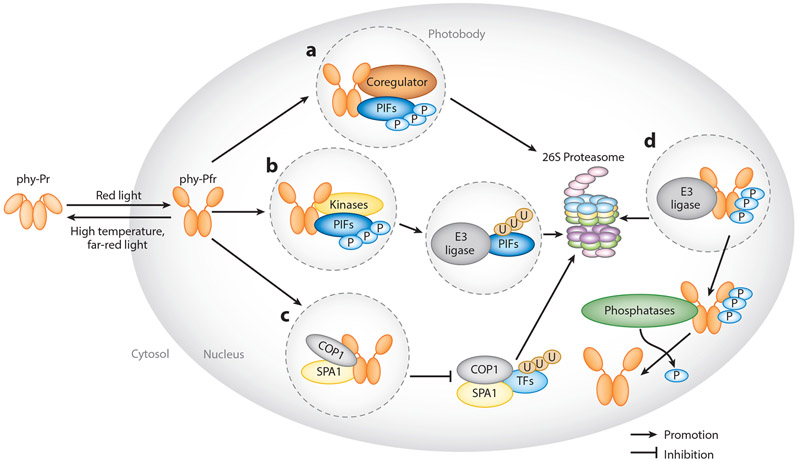
Figure 2.
Models of phytochrome signaling pathways regulated by their interacting proteins. (a) Phytochrome signaling proteins regulate the size and stability of photobodies. Formation of these photobodies (shown inside dashed circles) are promoted independently by coregulators such as PCH1, PCHL, HMR, NCP, and RCB. (b) Photobodies are also sites for the degradation of PIFs. phyB,PIFs, and kinases, such as PPKs and SPAs, colocalize within the photobodies, resulting in the phosphorylation of PIFs. PIFs are subsequently ubiquitinated and degraded. (c) phyA and phyB colocalize with SPA1 within the photobodies to sequester SPA1 from COP1, suppressing COP1 activity. (d) Phosphorylated phytochromes are also targets of the COP1/SPA1 complex and the E3 ligase LRB. Phytochromes are subsequently ubiquitinated and degraded. Phosphorylated phytochromes can be dephosphorylated by phosphatases, such as FyPP and PAPPs. Abbreviations: FR, far red; FyPP, FLOWER-SPECIFIC PHYTOCHROME-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE; phy, phytochrome; R, red; TF, transcription factor.