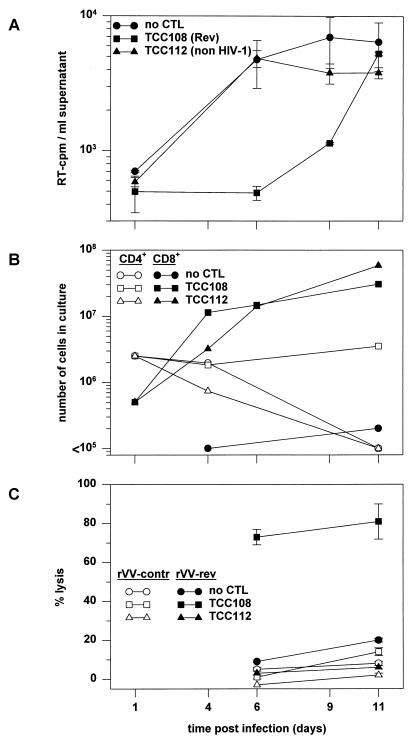
FIG. 4.
Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by Rev-specific CTL. HLA-B14-expressing PBMC from an HIV-seronegative individual were infected with HIV-1 IIIB as indicated in Materials and Methods. PBMC (5 × 106) were cocultivated without CTL, with 5 × 105 Rev-specific TCC108 cells, or with 5 × 105 non-HIV-specific TCC112 cells. Both types of TCC cells had been stimulated 7 days before addition to the PBMC. (A) Virus production was analyzed by quantification of the RT activity in culture supernatants. The average RT activity (with standard error) for triplicates is shown. (B) The fates of the CD4+ PBMC and the CD8+ TCC108 and TCC112 cells were determined by counting of the cells and flow cytometric analysis of membrane-expressed CD4, CD8, and HLA-A2. HLA-A2 was included to discriminate between CD8+ PBMC (expressing HLA-A2) and the added TCC108 and TCC112 cells (both expressing HLA-A1 and -A28). (C) CD8+ cells were recovered from the cultures on days 6 and 11 by magnetic bead selection and analyzed for Rev-specific CTL activity on autologous B-LCL cells infected with rVV-rev or rVV-control. The average percent specific lysis (with standard error) for triplicates is shown.