Figure 3 |. Advancements in prime editing systems.
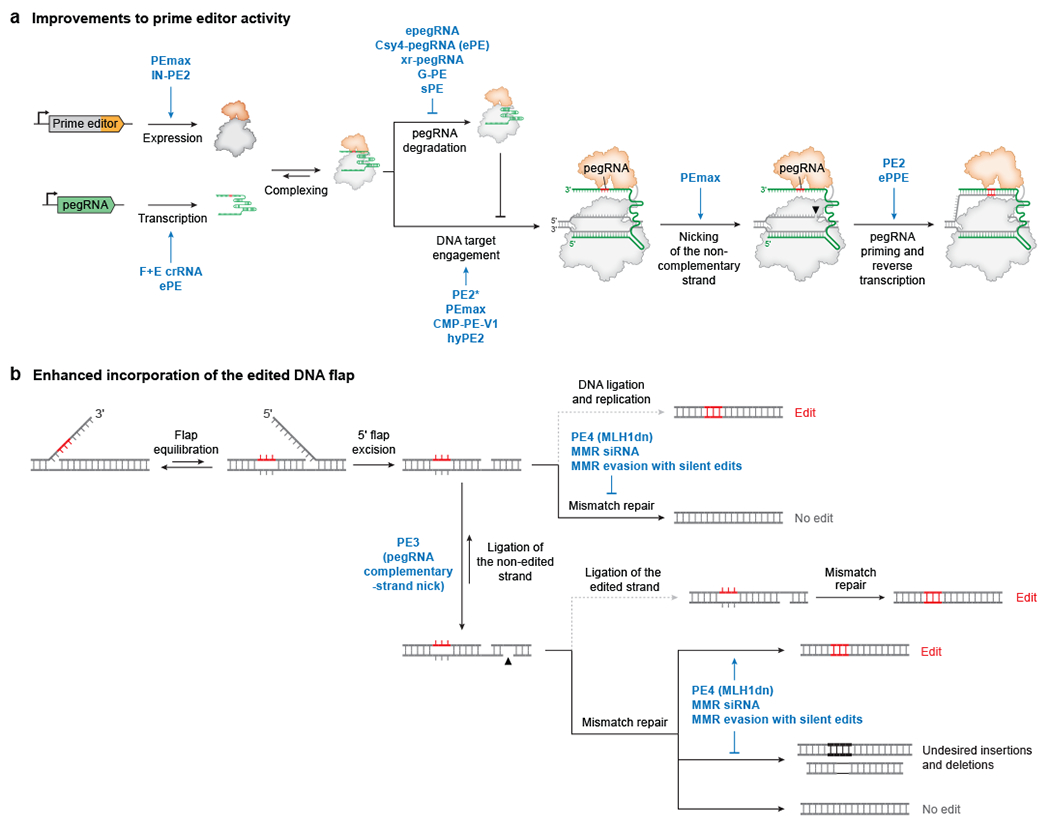
a | Variants of prime editors or prime editing guide RNAs (pegRNAs) that ultimately enhance the creation of the edited 3ʹ DNA flap. PEmax53, IN-PE270, pegRNAs carrying the F+E crRNA scaffold54,78, and ePE pegRNAs77 improve prime editor and pegRNA expression. epegRNAs54, ePE pegRNAs77, xr-pegRNAs74, G-PE pegRNAs75, and sPE pegRNAs76 reduce pegRNA degradation. PE2*68, PEmax53, CMP-PE-V163, and hyPE271 improve localization and/or DNA targeting of the prime editor complex. PEmax53 improves nicking of the genomic DNA strand. ePPE assists pegRNA-primer annealing72. The engineered MMLV RT in PE252 strongly enhances DNA flap synthesis. b | Strategies that promote permanent incorporation of the edited 3ʹ flap into genomic DNA. DNA ligation of the 3ʹ nicked heteroduplex intermediate followed by DNA replication successfully incorporates the desired prime edit, but mismatch repair of this intermediate excises and replaces the edited strand, resulting in no prime editing. Nicking the non-edited DNA strand with PE3 promotes copying of the edit to both genomic strands52. Cellular mismatch repair excises the nicked strand of DNA heteroduplexes, commonly leading to removal of the edit. Transient inhibition of mismatch repair with MLH1dn (PE4 and PE5)53 or with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs)53,59, or mismatch repair evasion through judicious design of the 3ʹ flap53, enhances conversion to the desired prime editing product and reduces undesired formation of small insertions or deletions (indels).
