Figure 4.
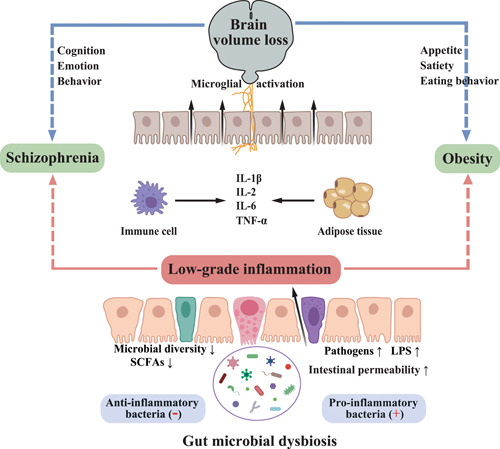
Gut‐derived inflammation as a potential hub linking schizophrenia and obesity. Gut microbial dysbiosis has been observed in both SZ and obesity. It leads to impaired intestinal barrier and thereby increased transport of pathogens and LPS to the circulatory system, resulting in the production of proinflammatory cytokines and elevated inflammation in the circulation. Peripheral cytokine signaling can induce neuroinflammation, leading to structural remodeling of the brain (manifested as brain volume loss), which can lead to changes in cognition, emotion, and behavior, as well as changes in appetite, satiety and eating behavior. IL‐1β, interleukin 1β; IL‐2, interleukin 2; IL‐6, interleukin 6; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; SCFAs, short‐chain fatty acids; SZ, schizophrenia; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor α.
