Figure 3.
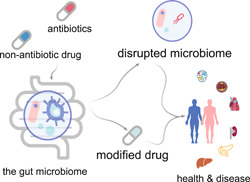
Microbial interactions with drugs. The gut microbiome can influence human health and disease through bidirectional interactions with drugs. On one hand, antibiotics can kill most of the gut bacteria that play important roles in maintaining the metabolic health of the host via a series of mechanisms. On the other hand, commonly used nonantibiotic drugs can be influenced by the gut microbiome via an enzymatic transformation that changes their bioavailability, bioactivity, or toxicity
