Figure 3.
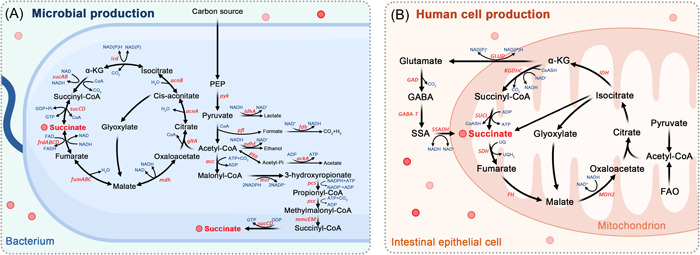
Biosynthetic pathways of succinate production in human cells and gut microbiota. (A) Succinate is commonly generated through a partial branch of the TCA cycle in microbial carbohydrate fermentation. The TCA cycle is present in nearly all microorganisms. Additionally, succinate can be produced through the glyoxylate shunt pathway and the 3‐hydroxypropionate pathway. (B) Succinate is an essential intermediate in the TCA cycle, which occurs in the mitochondria of host cells through a series of enzyme‐mediated reactions. In cells relying on anaerobic glycolysis or experiencing hypoxic conditions, alternative metabolic pathways are activated, leading to the accumulation of mitochondrial succinate. These pathways include the reductive branch of the TCA cycle through reverse succinate dehydrogenase activity, the GABA shunt, and glutamine‐dependent anaplerosis. acc, acetyl‐CoA carboxylase; ackA, acetate kinase; acnAB, aconitase; adhE, alcohol dehydrogenase; FAO, fatty acid oxidation; fdh, formate dehydrogenase; FH, fumarate hydratase; frdABCD, succinate dehydrogenase; fumABC, fumarate hydratase; GABA, γ‐aminobutyric acid; GABA‐T, GABA transaminase; GAD, glutamate decarboxylase; gltA, citrate synthetase; GLUD, glutamate dehydrogenase; icd, isocitrate dehydrogenase; IDH, Isocitrate dehydrogenase; ldhA, lactic dehydrogenase; KGDHC, ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex; mcr, malonyl‐CoA reductase; MDH2, malate dehydrogenase isoform 2 (mitochondrial); mdh, malate dehydrogenase; mmcEM, methylmalonyl‐CoA epimerase and mutase; PEP, Phosphoenolpyruvic acid; pcc, propionyl‐CoA carboxylase; pcs, propionyl‐CoA synthase; pfl, pyruvate formate lyase; pta, phosphotransacetylase; pyk, pyruvate kinase; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; SUCL, succinate‐CoA ligase; sucABCD, succinyl‐CoA synthetase; SSA, succinate semialdehyde; SSADH, succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase; UQ, Ubiquinone; UQH2, Ubiquinol; α‐KG, alpha‐ketoglutarate.
