Figure 4.
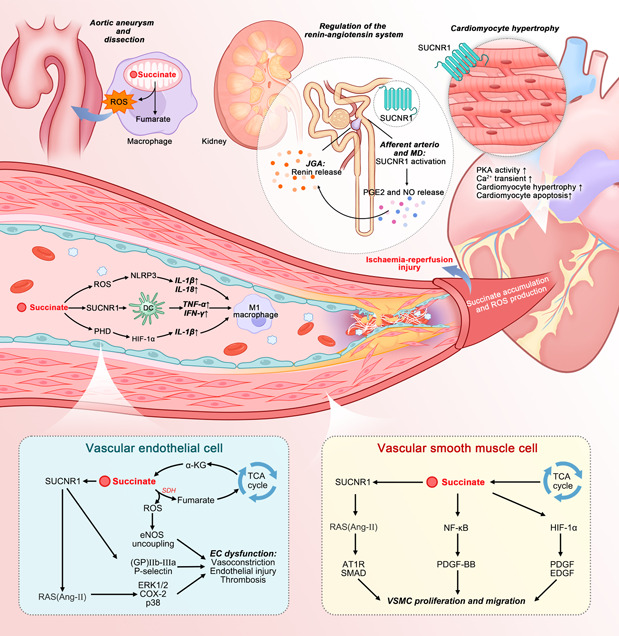
Effect of succinate on CVDs. Current research suggests the pleiotropic functions of succinate in vascular endothelial injury, VSMC growth and invasion, ischemia–reperfusion injury, macrophage polarization, aortic aneurysm and dissection, regulation of the renin‐angiotensin system, and cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, among others. Briefly, succinate can induce ROS in macrophages, promoting aortic aneurysm and dissection. It can also exacerbate endothelial cell dysfunction by upregulating ROS levels, which impairs the vasodilative effect of nitric oxide, activates RAS, and enhances thrombosis (shown in the blue rectangle at the bottom left). Accumulated succinate can stimulate SMC growth and invasion through RAS activation, HIF‐1α accumulation, and NF‐kB pathway promotion (shown in the yellow rectangle at the bottom right). In addition, succinate stimulates dendritic cells and macrophages to produce pro‐inflammatory cytokines, aggregating atherosclerosis. The interaction between succinate and SUCNR1 can disrupt the negative feedback loop of angiotensin II, contributing to hypertension and promoting cardiac hypertrophy via PKA pathway activation, Ca2+ transient, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Finally, accumulated succinate can drive ROS production at complex I, inducing ischemia‐reperfusion injury. Ang‐II, angiotensin II; AT1R, angiotensin II type‐1 receptor; COX‐2, cyclooxygenase‐2; DC, dendritic cell; EC, endothelial cell; EDGF, epidermal growth factor; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthases; ERK1/2, extracellular signal‐regulated kinase 1/2; GP, glycoprotein; HIF‐1α, hypoxia‐inducible factor 1‐alpha; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; JGA, juxtaglomerular apparatus; MD, macula densa; NF‐kB, nuclear factor kappa beta; NLRP3, Nod‐like receptor 3; NO, nitrogen monoxide; PDGF‐BB, platelet‐derived growth factor‐BB; PGE2, prostaglandin E2; PHD, prolyl hydroxylase domain; PKA, protein kinase A; RAS, renin–angiotensin system; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SDH, succinate dehydrogenase; SMAD, drosophila mothers against decapentaplegic protein; SUCNR1, succinate receptor 1; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell; α‐KG, alpha‐ketoglutarate.
