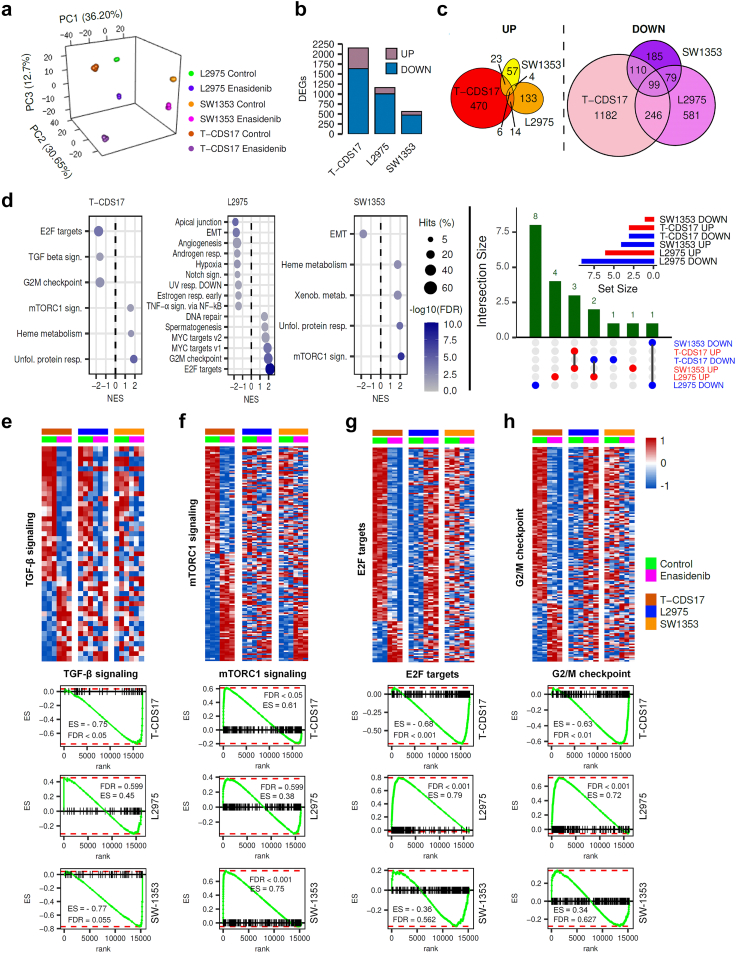
Fig. 5.
Effect of enasidenib on the transcriptome of IDH2-mutant chondrosarcoma cells. T-CDS-17#1, SW1353 and L2975 cells were treated in biological triplicates with DMSO (control) or 20 μM enasidenib for 48 h prior to be processed for RNA sequencing. (a) Principal component analysis of all samples according to rlog expression values in the top 1000 most variable genes between control and treatment conditions for each cell type. (b) Bar plot depicting the number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs, FDR <0.05 and |log2 (FC)|>1) that were up- or down-regulated in each cell type by enasidenib treatment. (c) Venn diagrams showing the intersections between DEGS upregulated (left panel) and downregulated (right panel) by enasidenib in T-CDS-17#1, SW1353 and L2975 cells. The list of genes commonly upregulated and downregulated in the different cell lines is presented in Tables S5 and S6 respectively. (d) Bubble plots (left panels) showing significantly enriched pathways (GSEA, FDR <0.05) from the MSigDB Hallmark collection in each enasidenib-treated cell type. Upset plot (right panel) depicting intersections of significantly enriched pathways (FDR <0.05) in T-CDS17, L2975 and SW1353 cell lines. Set size of pathways up downregulated in each cell line is showed as an inset. (e–h) Top panels: heatmap plots showing the expression values of those DEGs (FDR <0.05) of the Hallmarks TGFβ (e), mTORC1 (f), E2F targets (g) and G/M checkpoint (h) signalling pathways. Bottom panels: GSEA analysis of these signalling pathways in the indicated cell lines. Enrichment score (ES) and False discovery rate (FDR) values are indicated.