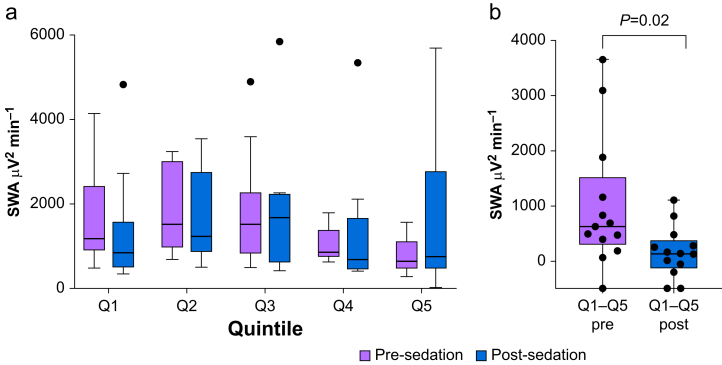
Fig 4.
Dexmedetomidine sedation dosed to induce EEG slow waves alters rate of dissipation of SWA. (a) Boxplot comparing sleep SWA measures in different quintiles comparing pre- and post-sedation. Black dots represent individual data points falling outside of the upper fence of the Tukey box plots. Sleep pressure measured as SWA in the first quintile was not significantly different between pre- and post-sedation (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, P=0.27). (b) Comparison of SWA dissipation across the entire night expressed as the first quintile (Q1) minus the last quintile (Q5) for pre- and post-sedation. SWA dissipation was significantly reduced post-sedation compared with pre-sedation (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, P=0.02). SWA, slow wave activity.