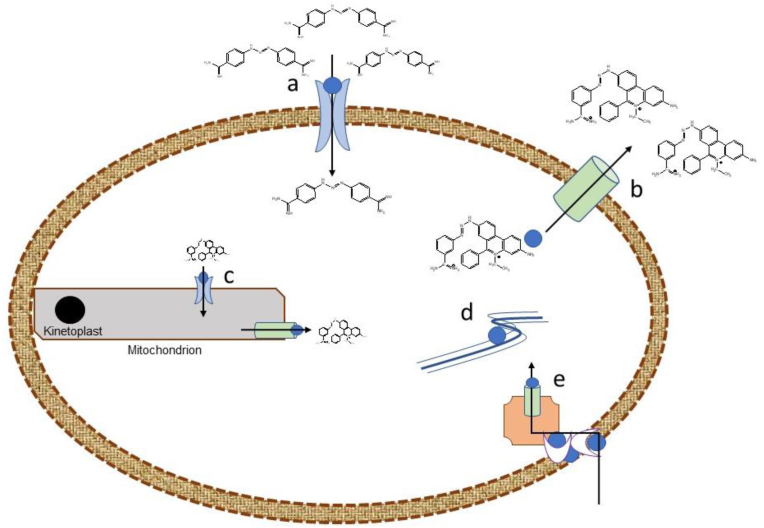
Fig. 1.
Illustration of drug action and resistance mechanisms in trypanosomes.
A. Drug importer such as P2/AT1 transporter for diamidines. B. Drug efflux pump such as multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRAP) in resistance to melaminophenyl arsenicals. C. Mechanisms that relate to delivery and accumulation in or efflux of drug from target organelle such as mitochondrion which houses the kinetoplast, which in itself is a target of multiple trypanocides. E. Surface binding protein, endocytic mechanism or a transporter that delivers endocytosed drug to the cell membrane such as a lysosomal transporter in suramin action. F. Target organelle or molecule that drug binds to. Disruption of these drug transport or action mechanisms may result in drug resistance.