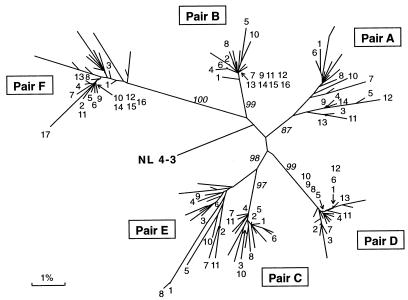
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of vpr sequences from six mother-infant pairs (A, B, C, D, E, and F). The distances were calculated between the nucleotide sequences from the six mother-infant pairs. Each leaf of the tree represents one vpr sequence. The mother sequences in each pair are labeled with the number of the clones (Fig. 1), whereas the infant sequences are unlabeled. The tree was rooted by using the reference HIV-1 sequence, NL 4-3 (37). The numbers at branch points indicate the occurrence number of branches over 100 bootstrap resampling of the data sets. The mother-infant pairs formed a distinct cluster and are discriminated, separated, and confined within subtrees, indicating the absence of PCR product cross-contamination (21, 24).