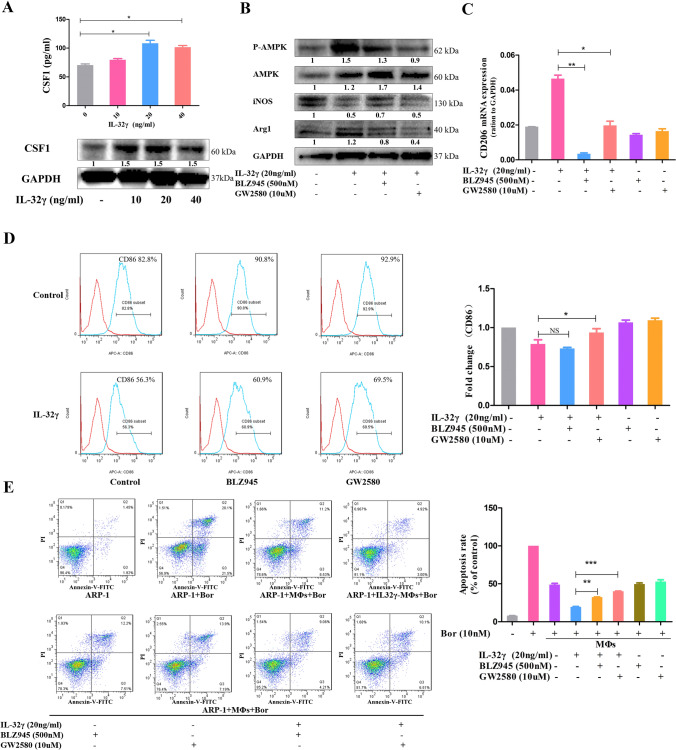
Fig. 4.
CSF1 is crucial in IL-32γ-induced M2 MΦ polarization and drug resistance. a MΦs were stimulated with different concentrations of IL-32γ (10, 20 and 40 ng/mL) for 24 h, ELISA was used to detect the content of CSF1 in the cell culture supernatant, and Western blotting was adopted to evaluate the protein level of CSF1 in MΦs. Summarized results from at least three independent experiments are shown. Values are presented as means ± SEM. b MΦs were pretreated with a CSF1 receptor inhibitor (500 nM BLZ945 or 10 μM GW2580) for 2 h and then stimulated with IL-32γ (20 ng/mL) for 24 h. The expression of iNOS, p-AMPK and Arg1 was detected by Western blotting. The quantified density is shown below the bands. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. c qRT-PCR was used to detect changes in CD206 expression, and summarized results from at least three experiments are shown. Values are presented as means ± SEM. d Representative and summarized results for flow cytometry analysis of CD86 expression. The summarized results are from at least three independent experiments. Values are presented as means ± SEM. e MΦs were treated as above and then cocultured with ARP-1 cells in suspension and Bor (10 nM) for 24 h. The ARP-1 cells were collected, and apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. Values are presented as means ± SEM. NS, not statistically significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01