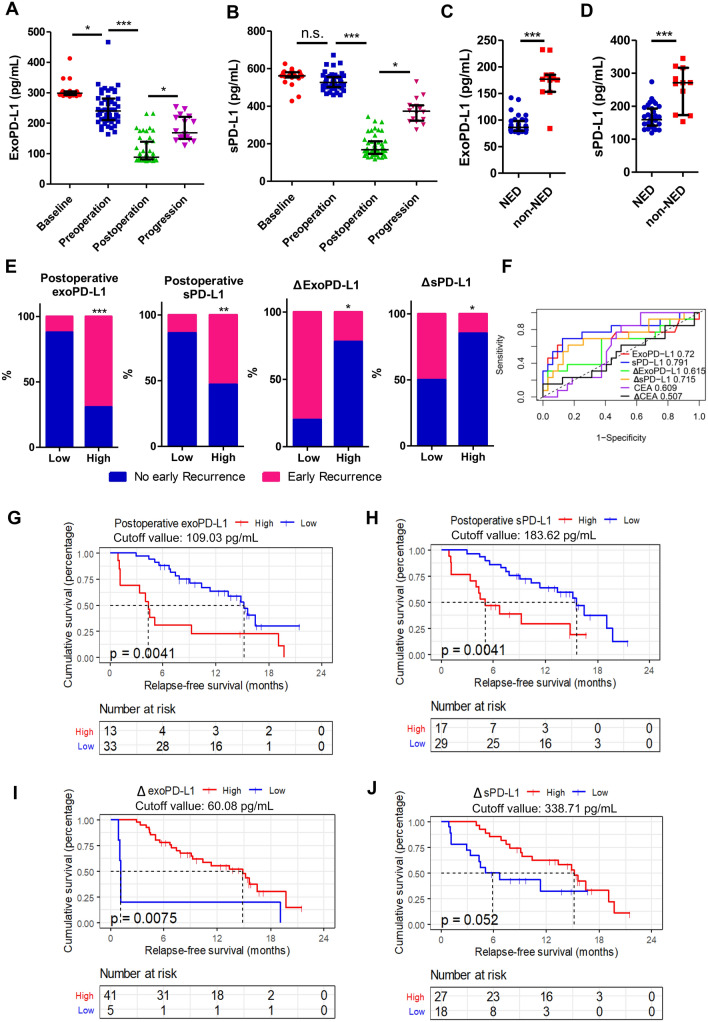
Fig. 4.
Association between dynamic changes in circulating PD-L1 level and CRLM disease status as well as early recurrence. A Different sPD-L1 expression levels according to patients’ disease status: sPD-L1 level is significantly higher at baseline and preoperatively and decreases postoperatively and increases when disease progressed; B different exoPD-L1 levels according to patients’ disease status: exoPD-L1 level is highest at baseline and decreases preoperatively, there is a further reduction after surgery and an increment when disease progressed; C SPD-L1 is significantly higher in patients with non-NED status compared to NED status; D ExoPD-L1 is significantly higher at non-NED status compared with NED status; E early recurrence rate according to the different expression levels of postoperative exoPD-L1, postoperative sPD-L1 and expression level change of exoPD-L1 and sPD-L1 before and after hepatectomy; F ROC curves of postoperative exoPD-L1, sPD-L1, CEA or changes of exoPD-L1, sPD-L1 and CEA before and after hepatectomy to predict early recurrence; Kaplan–Meier estimation of relapse-free survival in patients according to G postoperative exoPD-L1 (p = 0.0041); H postoperative sPD-L1 (p = 0.0041); I changes of exoPD-L1 (p = 0.0075) and J sPD-L1 (p = 0.052) before and after hepatectomy. n.s., no significance; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001