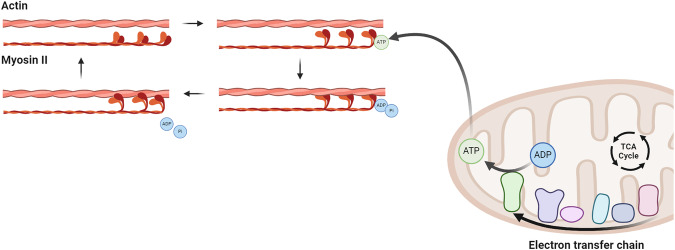
Fig. 1. Working mechanism behind myofibroblast contraction.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is produced by the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle and electron transfer chain and binds to an unattached myosin head. Here, it is hydrolysed and causes the myosin head to form a cross-bridge. Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi) release causes the myosin head to change position and the actin filament to thereby move causing myofibroblast contraction. Created with BioRender.com.