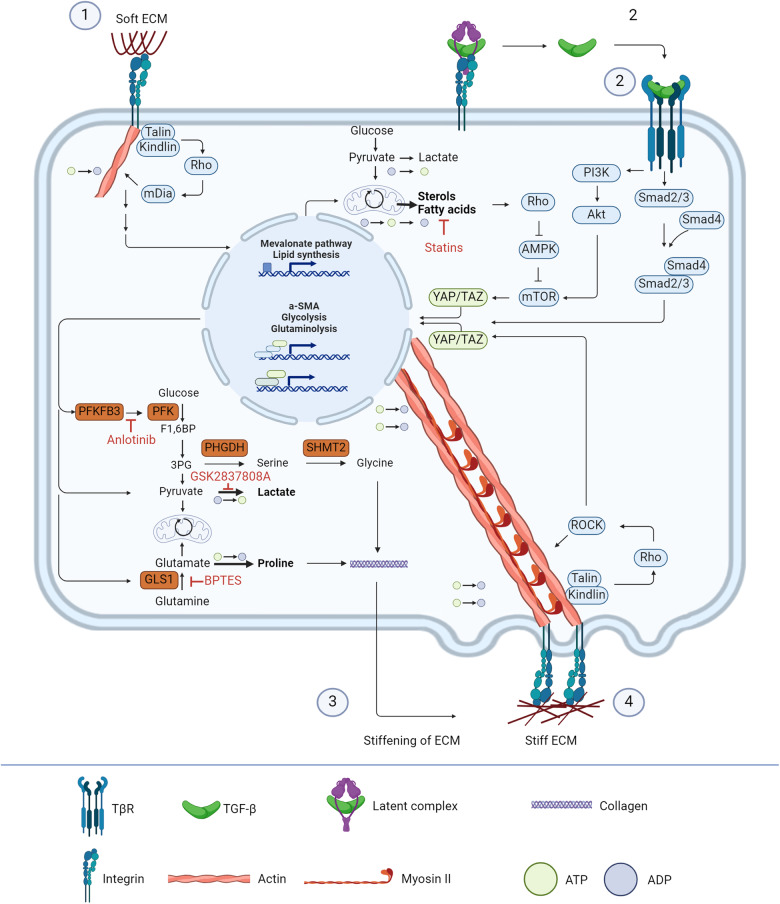
Fig. 5. Overview of cellular metabolism and myofibroblast contraction cascades.
Soft ECM causes signalling through the Rho-mDia axis, which is often paired with the assembly of actin filaments and upregulation of the mevalonate pathway. Additionally, the same integrin receptors can bind the latency complex of TGF-β thereby causing release of the mature ligand. This, together with YAP/TAZ, then takes over the actin filament synthesis and by increasing the expression of key enzymes in the glycolysis and glutaminolysis the TGF-β and YAP/TAZ axis produce stiffer ECM. Stiff ECM causes the integrin signalling to shift to the Rho-ROCK axis, which is paired with myosin II synthesis and subsequently contraction. Additionally, ROCK promotes YAP/TAZ to be localised in the nucleus to promote a feedforward loop towards stiff ECM and myofibroblast contraction. By inhibiting key points in the feedforward loop, such as the mevalonate pathway with statins109–112, glycolysis with Anlotinib104, lactate production by GSK2837808A106, or glutaminolysis with BPTES107,108, it might be possible to break the loop and thereby switch the fibrotic cascades back to regenerative cascades.