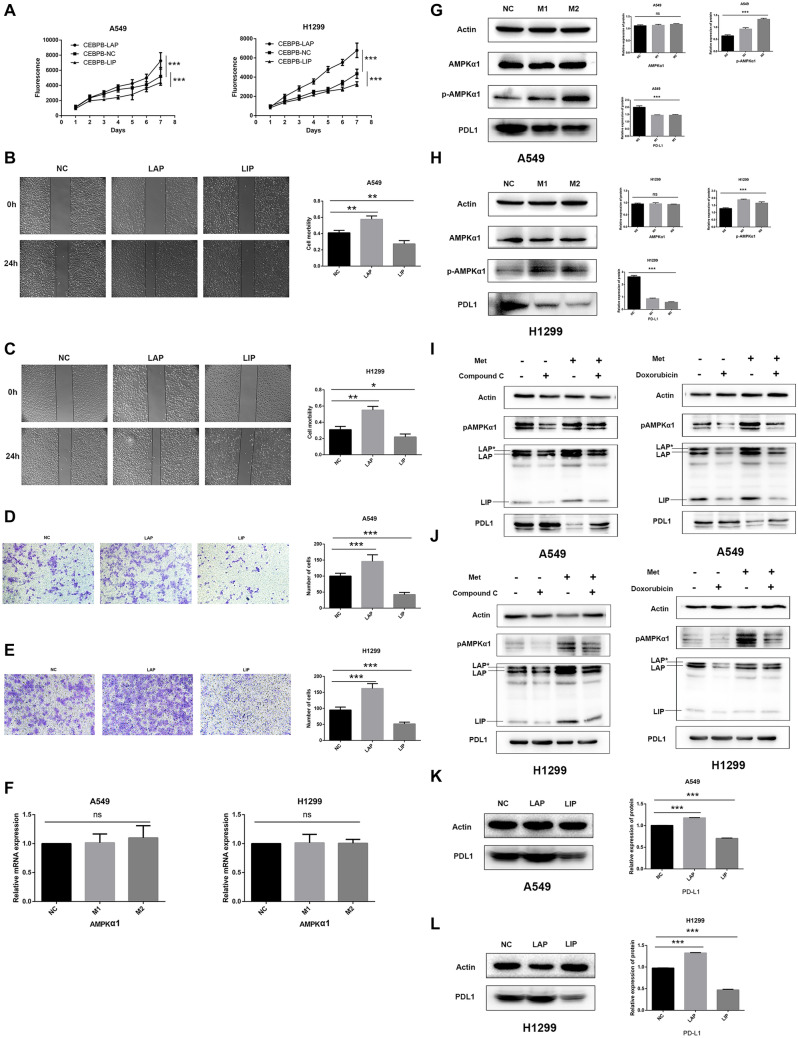
Fig. 3.
Metformin inhibited NSCLC through AMPK–CEBPB–PDL1 signaling pathway. A The proliferation of LAP-OE cells increased significantly (P < 0.05), and the proliferation of LIP-OE decreased significantly (P < 0.001) compared with NC cells. b, C The mobility of LAP-OE was significantly increased, while the mobility of LIP-OE was significantly decreased. D, E The cell migration of LAP-OE significantly increased, while the cell migration of LIP-OE significantly reduced. F No significant change in AMPKα1 mRNA expression was observed after being treated by metformin by qPCR. G, H The phosphorylation level of AMPKα1 (pAMPKα1) was significantly increased (P < 0.001), and the PDL1 protein was significantly downregulated in 549 cells and H1299 cells treated with metformin (P < 0.001). I, J After the addition of AMPK inhibitor (Compound C and Doxorubicin) in A549 cells and H1299 cells, AMPKα1 phosphorylation was significantly downregulated, and the expression of three isoforms of CEBPB, namely LAP*, LAP, and LIP, were all downregulated, while the expression of PDL1 was upregulated. The metformin reversed the inhibitory effect of AMPK inhibitors. K, l Western blot analysis showed that PDL1 expression was significantly increased LAP-OE cells, but was significantly downregulated in LIP-OE cells (P < 0.001). Metformin concentration. NC: no metformin treatment. M1: 0.15 mmol/L (A549), 1 mmol/L (H1299). M2: 0.25 mmol/L (A549), 2 mmol/L (H1299)