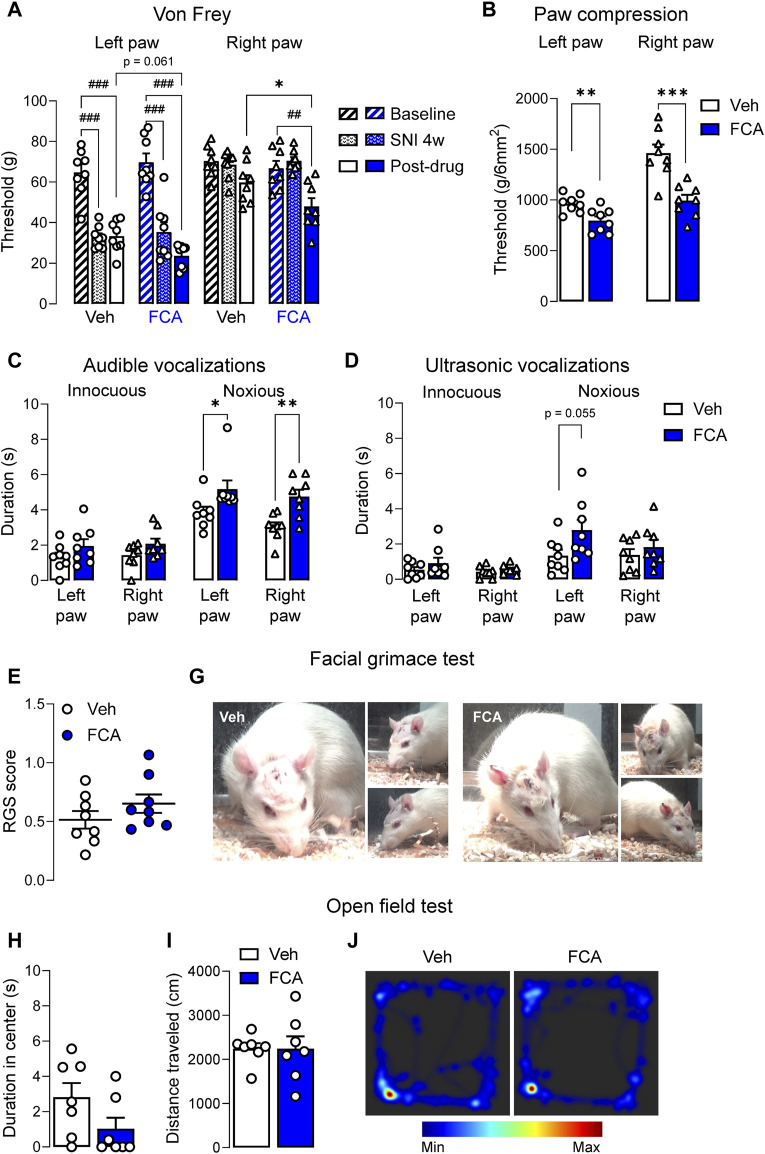
FIGURE 4.
Pronociceptive effects of astrocyte inhibition by FCA in CeA on neuropathic pain-like behaviors. (A) Mechanical thresholds (measured by electronic von Frey) of the left (injured), but not right, hind paw were significantly decreased 4 weeks after SNL surgery, confirming the neuropathic pain condition. Stereotaxic injection of FCA (100 μM, 1 μL) into the CeA significantly lowered mechanical withdrawal thresholds on the right hind paw and further decreased the thresholds on the left hind paw compared to vehicle (Veh) treatment. Bar histograms show mean ± SEM. ##, ### p < 0.01, 0.001 compared to baseline (pre-SNL surgery). *, p < 0.05, compared to vehicle, two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons. Intra-CeA administration of FCA (100 μM, 1 μL) significantly decreased the withdrawal thresholds measured by compression (B) of the left (injured) and right paws and increased the audible vocalizations (C) evoked by noxious, but not innocuous, stimulation of the left (injured) and right hind paws, but had no significant effect on the ultrasonic vocalizations (D) though a trend for a facilitatory effect was observed for the noxious compression of the left (injured) hind paw. Injection of FCA (100 μM, 1 μL) into the CeA showed a non-significant trend to facilitatory effects on the facial grimace scale (E,G) and anxiety-like behaviors measured in the open field test (H–J) compared to vehicle. Bar histograms show mean ± SEM. *, **, ***p < 0.05, 0.01, 0.001 compared to vehicle, unpaired student t-tests. (A-G) Veh, n = 8; FCA, n = 8; (H-L) Veh, n = 7; FCA, n = 7.