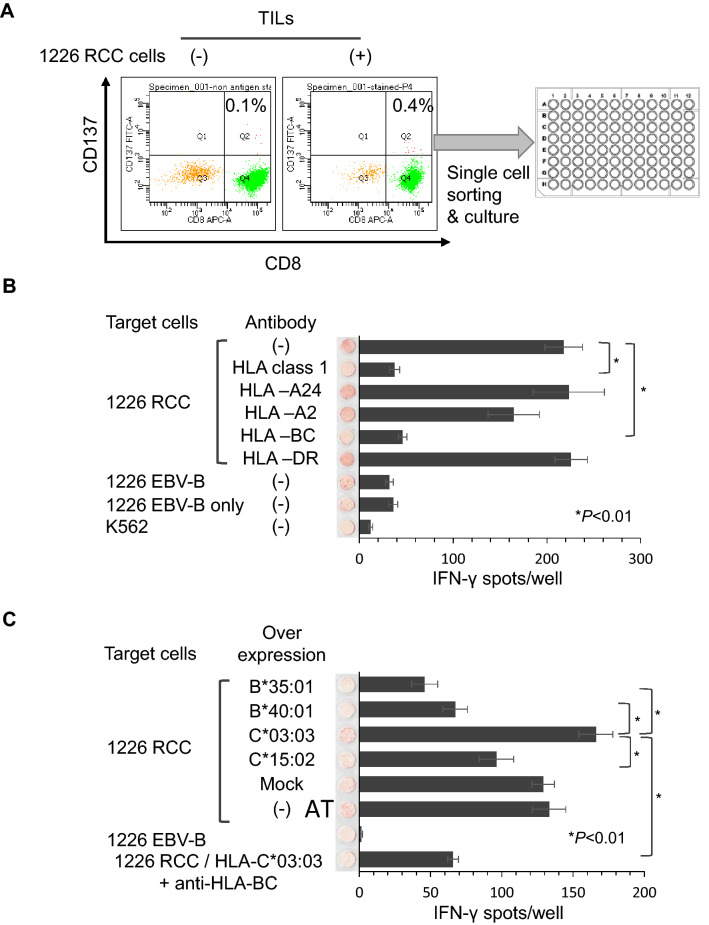
Fig. 2.
Establishment of the reactive 1226 RCC TIL clone. a. TIL clone establishment method. TILs obtained from the red tumor were stained with anti-CD8 and anti-CD137 antibodies. TILs were co-cultured with 1226 RCC cells before FACS analysis. TILs without co-culture were used as a negative control. CD137+ cells were single cell-sorted using a cell sorter. After several weeks of in vitro culture, 116 of 384 clones showed cell growth. b IFNγ ELISPOT assay of the Q1 TIL clone. Q1 TIL clones were co-cultured with 1226 RCC cells and analyzed by an IFNγ ELISPOT assay. Anti-HLA-pan class 1 (W6/32), anti-HLA-A24 (C7709A2.6), anti-HLA-A2 (BB7.2), anti-HLA-BC (B1.23.2), and anti-HLA-DR (L243) antibodies were used to assess the specific reactivity of the Q1 TIL clone. 1226 EBV-B cells and K562 cells were used as negative controls. IFNγ spots are shown as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM; n = 3), and p values were calculated using a paired t test; *p < 0.01. c IFNγ ELISPOT assay of the Q1 TIL clone using HLA allele-specific over-expressing 1226 RCC cells. HLA-B*35:01, B*40:01, C*03:03, and C*15:02 were stably over-expressed in 1226 RCC cells. Q1 TIL clone reactivity for HLA alleles over-expressed in 1226 RCC cells was examined by an IFNγ ELISPOT assay. An anti-HLA-BC (B1.23.2) antibody was used to confirm specificity. IFNγ spots are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 3), and p values were calculated using a paired t test; *p < 0.01