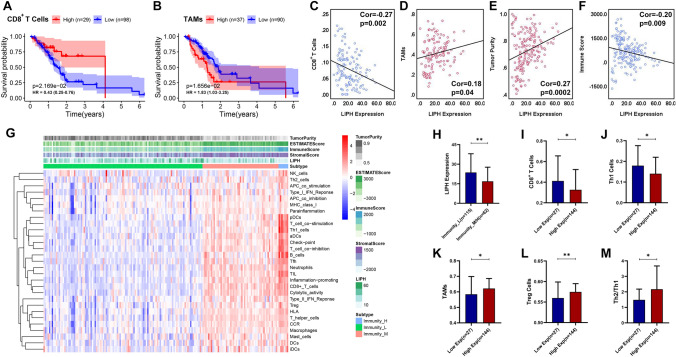
Fig. 6.
Association between LIPH expression and the immune infiltration within tumors in TCGA dataset. A KM survival analysis showed that patients with lower infiltration levels of CD8+ T cells had a short OS than those with higher infiltration levels of CD8+ T cells (P < 0.05). B Patients with higher infiltration of macrophages had a shorter OS (P < 0.05) than those with lower infiltration of TAMs (P < 0.05). C LIPH expression negatively correlated with the infiltration level of CD8+ T cells (Cor = − 0.27, P < 0.01). D LIPH expression positively correlated with the infiltration level of TAMs (Cor = 0.18, P < 0.05) and E tumor purity (Cor = 0.27, P < 0.001). F LIPH expression negative correlated with immune score (Cor = − 0.20, P < 0.01). G Based on the ssGSEA analysis, the enrichment scores of 29 immune-related term were obtained and 177 PC samples in TCGA PC dataset were divided into the immunity L (n = 115), immunity M (n = 55), and immunity H (n = 7) groups. H LIPH expression was significantly upregulated in the immunity-L group compared with the immunity-M/H group. I LIPH overexpression was significantly associated with low infiltration levels of CD8+ T cells. J LIPH overexpression was significantly associated with low infiltration levels of Th1 cells, K high infiltration of TAMs, L Treg cells and M Th2/Th1. (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01;***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001). TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; Treg cells, regulatory T cells; Th1, type-1 T helper cells; type-2 T helper cells; ssGSEA, single sample gene set enrichment analysis; KM, Kaplan–Meier; OS, overall survival; Cor, pearson correlated coefficient