Figure 1.
Phylogeny and expression of Rhodnius prolixus TRPs
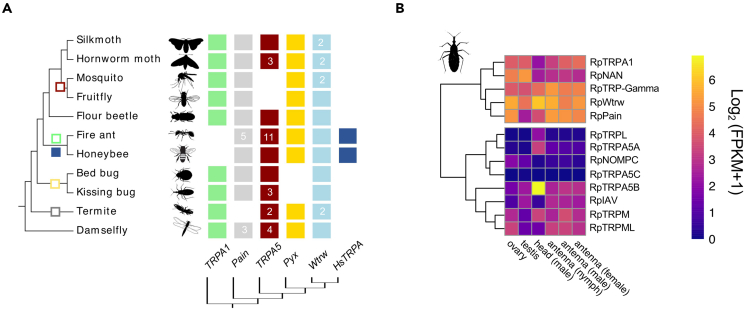
(A) Phylogenetic reconstruction of the ankyrin TRP (TRPA) channel subfamilies in representative insect species. TRPA5 channels are present across insect orders but absent from dipteran genomes (see also Table S1; Figures S1 and S2). Gene abbreviations: Painless (Pain), Pyrexia (Pyx), Waterwitch (Wtrw), TRPA Hymenoptera-specific (HsTRPA). Silkmoth, Bombyx mori; Hornworm moth, Manduca sexta; Mosquito, Anopheles gambiae; Fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster; Flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum; Fire ant, Solenopsis invicta; Honeybee, Apis mellifera; Bed bug, Cimex lectularis; Kissing bug, Rhodnius prolixus; Termite, Zootermopsis nevadensis; Bluetail Damselfly, Ischnura elegans. Gene gain: filled square; gene loss: empty square. Numbers within squares indicate gene number when different from 1.
(B) TRP genes in R. prolixus and their relative expression levels across tissues in compiled transcriptomic data (seeSTAR Methods). Heat maps compare the expression levels across tissues and developmental stages. Expression levels are represented as Log2 FPKM +1 and depicted with a gradient color scale. Gene models are based on genomic annotations,36 and de novo transcriptome assembly45 (see also Tables S2 and S3; Figure S3).