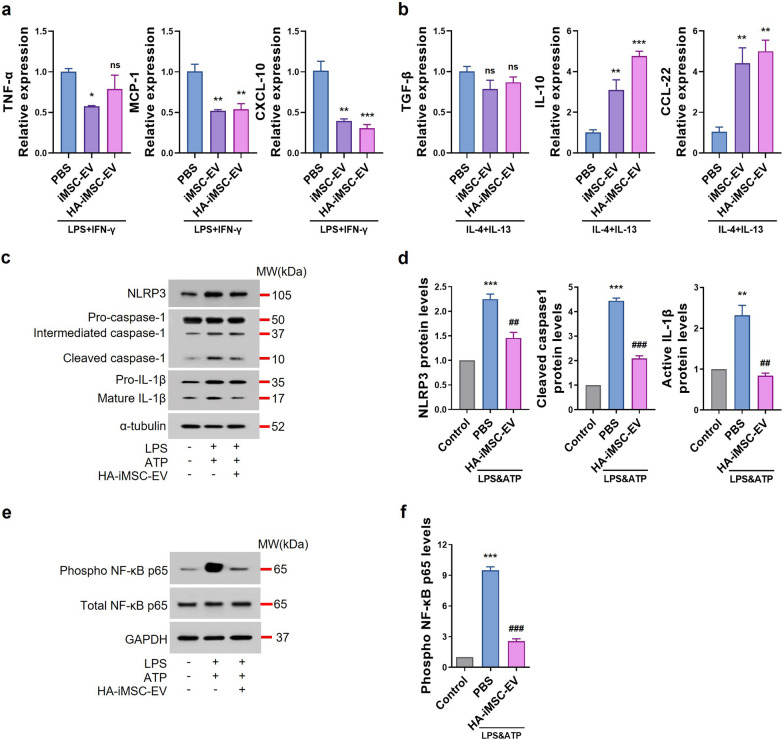
Fig. 3.
Anti-inflammatory effect of HA-iMSC-EVs on macrophages. a, b Effects of HA-iMSC-EVs on macrophage polarization of THP-1 cells treated with LPS and IFN-γ (a) or IL-4 and IL-13 (b). a Comparison of the relative mRNA expression levels of M1 polarization-related genes (TNF-α, MCP-1, and CXCL-10). b Comparison of relative mRNA expression levels of M2 polarization-related genes (TGF-β, IL-10, and CCL-22). Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns, not significant; one-way ANOVA. c–f Inflammasome-related protein expression in THP-1 cells treated with LPS, ATP, and HA-iMSC-EVs. c, d Western blot images represent that the inflammasome sensor protein NLRP3 and effector proteins caspase-1 and IL-1b were reduced by 400 μg/mL of HA-iMSC-EVs treatment in THP-1 activated by 1 ug/mL of LPS and 5 mM of APT (c) and the graphs show the quantitation results (d). Mean ± SE, n = 3, ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01 vs Control, ###p < 0.001; ##p < 0.01 vs PBS; one-way ANOVA. e, f Suppression of p65 phosphorylation in THP-1 macrophages treated with LPS and ATP using HA-iMSC-EVs. The protein levels of phosphorylated p65 decreased in THP-1 cells treated with HA-iMSC-EVs (e), and the graph shows the quantitation results (f). Mean ± SE, n = 4, ***p < 0.001 vs Control, ###p < 0.001 vs PBS; one-way ANOVA