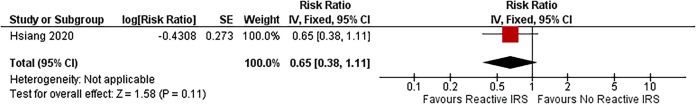
Figure 2.
Forest plot of comparison: reactive IRS versus no reactive IRS on the incidence of clinical malaria, superiority design. The authors calculated the effect size using marginal effects post-estimation (to account for reactive drug administration in half the clusters) after a regression model; thus, the 95% CI bounds are not balanced around the point estimate. Because the Review Manager software can only accommodate balanced CIs, the 95% CI contains the correct upper bound but is artificially narrow. IV = inverse variance; IRS = indoor residual spraying; SE = standard error.