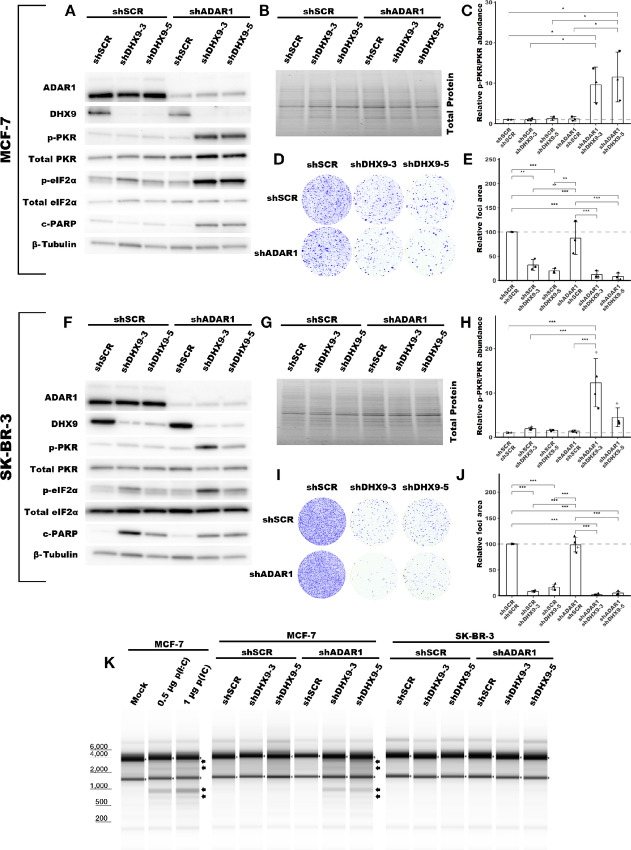
FIGURE 4.
DHX9 and ADAR1 redundantly suppress dsRNA sensing in ADAR1-independent cell lines. Representative immunoblot showing the phenotype of ADAR1 and/or DHX9 knockdown in MCF-7 (A), or SK-BR-3 (F). Immunoblots for other replicates and uncropped blots can be found in Source Data Figures. Protein abundance from the immunoblot in A and F was normalized by total protein abundance by quantification of the Stain-Free gel in B and G, respectively. Fold change of PKR phosphorylation at Thr-446 in MCF-7 (C) or SK-BR-3 (H) as determined by the immunoblots in A or F, respectively. Quantification of protein expression for other proteins of interest can be found in Supplementary Fig. S5A–S5L. Protein lysates were collected from cells five (MCF-7) or four (SK-BR-3) days after transduction with lentivirus encoding the shRNAs listed. Representative foci formation phenotype of ADAR1 and/or DHX9 knockdown in MCF-7 (D) or SK-BR-3 (I), quantification of relative foci area is shown in E or J, respectively. Cells were plated for foci formation 2 days after transduction and foci were stained when visible, 21 (MCF-7) or 10 (SK-BR-3) days later. K, Analysis of rRNA integrity upon knockdown of ADAR1 and/or DHX9 in MCF-7 or SK-BR-3. RNA was isolated from cells at the same time protein lysates were collected. In addition, K shows the effect of poly(I:C) [p(I:C)] transfection on rRNA integrity in MCF-7. Arrows indicate canonical RNase L cleavage products (64). Bars represent the average of at least three replicates, error bars are ± SD. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. P values determined by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey. Comparisons between the two different shRNAs targeting DHX9 (shDHX9-3 and shDHX9-5) were not included for clarity.