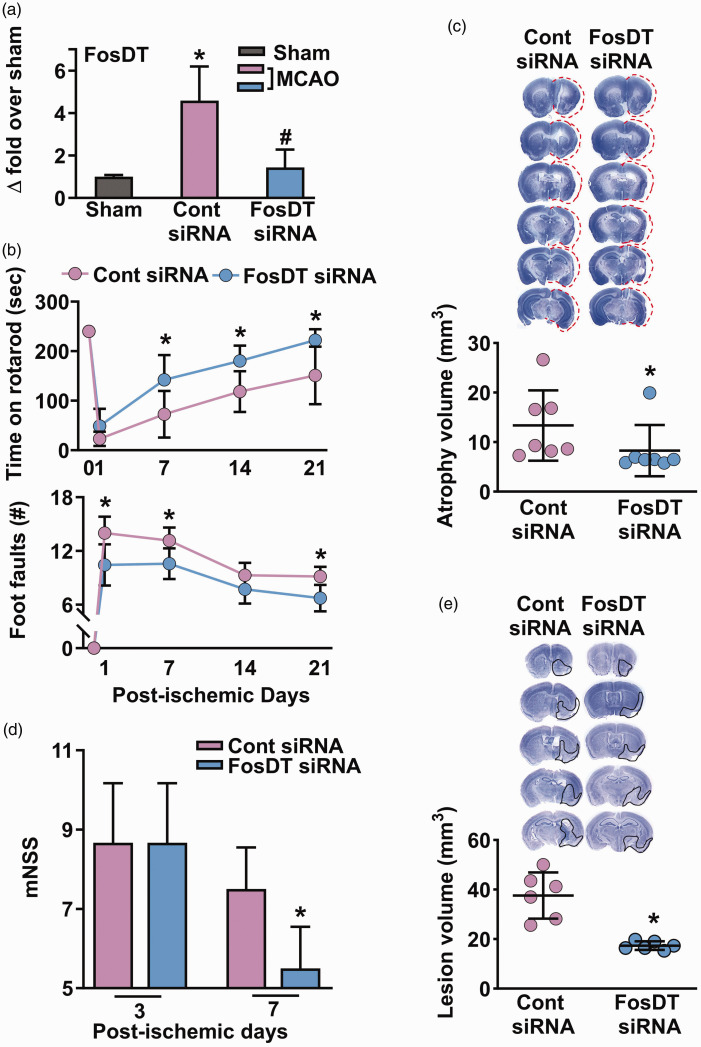
Figure 4.
FosDT siRNA also protected normal and type-2 diabetic mice subjected to transient MCAO. In the peri-infarct cortex of mice subjected to transient MCAO, FosDT expression increased significantly at 24 h of reperfusion compared with sham (a). FosDT siRNA significantly decreased post-ischemic FosDT levels compared with the control siRNA cohort (a). *p < 0.05 compared with sham and #p < 0.05 compared with control siRNA by Mann-Whitney U test (n = 4/group). In adult mice, FosDT siRNA treatment significantly improved motor function recovery between days 1 to 7 (b) and decreased infarct volume (c) at day 7 of reperfusion compared with the control siRNA cohort (b). FosDT siRNA administration also reduced the motor dysfunction (estimated by mNSS) on days 3 and 7 (d) and reduced the infarct volume on day 7 (e) in type-2 diabetic comorbid mice compared with the control siRNA cohort. Values are n = 7/group (a, b, and c) and n = 6/group (d and e). *p < 0.05 compared to the respective control siRNA group by repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's multiple comparisons test (b) or by Mann-Whitney U test (a, c, d, and e).