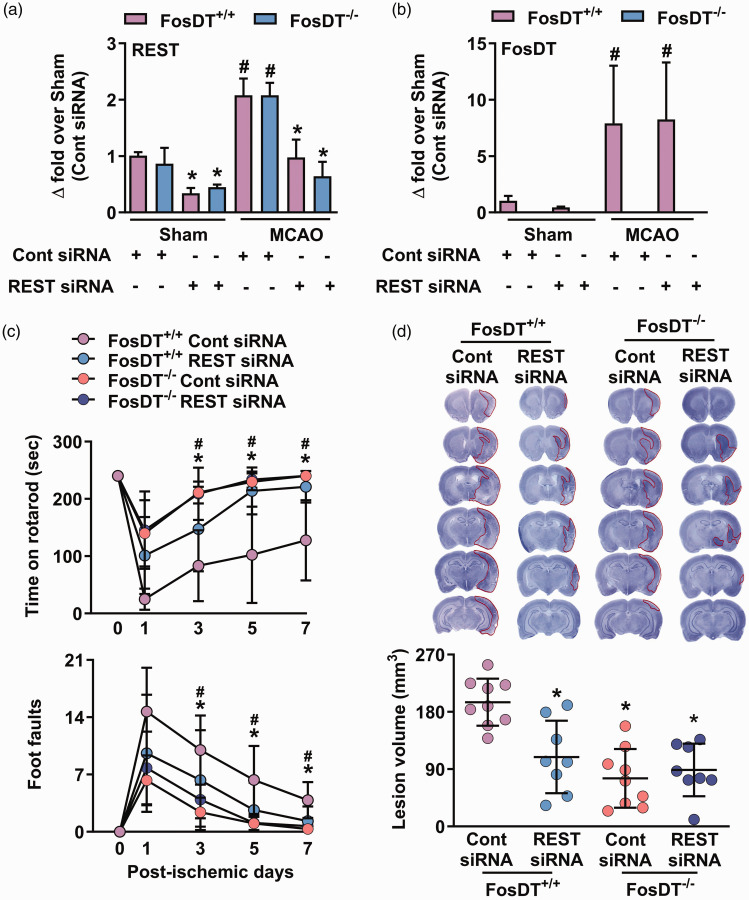
Figure 5.
FosDT is essential for REST function. When treated with REST siRNA (IV), expression of REST (a), but not FosDT (b), decreased significantly at 12 h in the peri-infarct cortex of FosDT+/+ and FosDT−/− rats subjected to sham surgery or transient MCAO, compared with respective control siRNA cohort. Values are mean ± SD (n = 3/group). *p < 0.05 compared with the respective control siRNA group and #p < 0.05 compared with the respective sham group by one-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons post-test. FosDT−/− rats showed improved motor function recovery and smaller infarcts compared with FosDT+/+ rats (c and d). REST siRNA treatment promoted motor function recovery (c) and smaller infarction (d) in FosDT+/+ rats but not in FosDT−/− rats, compared to respective control siRNA treated cohorts. *p < 0.05 vs FosDT+/+ control siRNA. Values (n = 8–9/group) are mean ± SD.