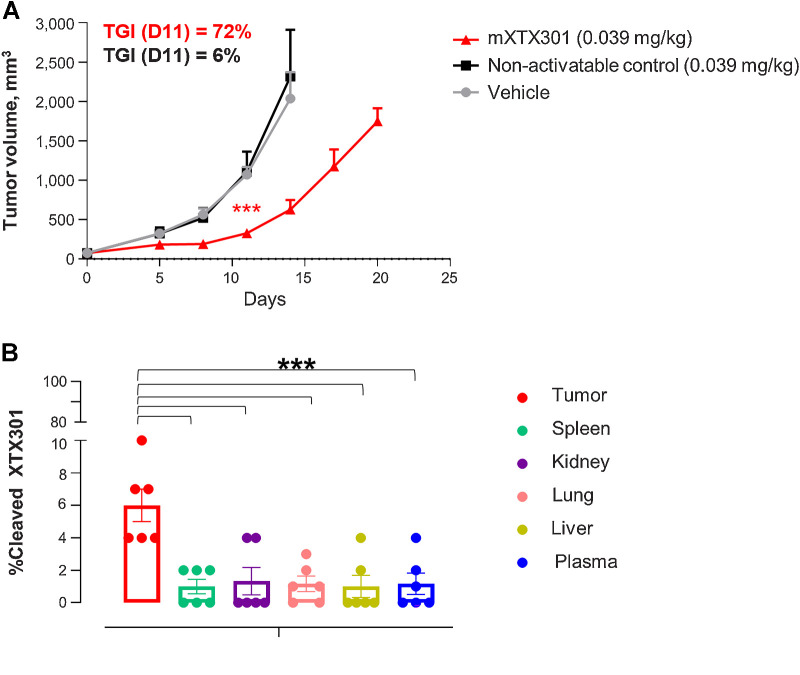
Figure 4.
TME-associated protease-dependent activation of mXTX301 in vivo(A) C57BL/6J mice were implanted subcutaneously with MC38 tumor cells and received a single intravenous injection of mXTX301, or non-activatable control lacking protease cleavage site at indicated dose levels. Data represent mean ± SEM. Tumor measurements were assessed by a two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc pairwise comparison test compared with vehicle (PBS) treated animals (***, P < 0.0005). The tumor growth changes are displayed until Day 14, when 86% of vehicle-treated animals were alive (N = 6). B, Measurement of percentage of cleaved mXTX301 in the tumor, peripheral organs, and plasma in the MC38 syngeneic tumor model. The percentage of cleaved mXTX301 was quantified by fluorescent triplex WB (LLOQ is represented by the dotted line) The data represents mean ± SEM. Statistical comparisons were performed using Dunnett ordinary one-way ANOVA test versus tumor, where ***, P < 0.001.