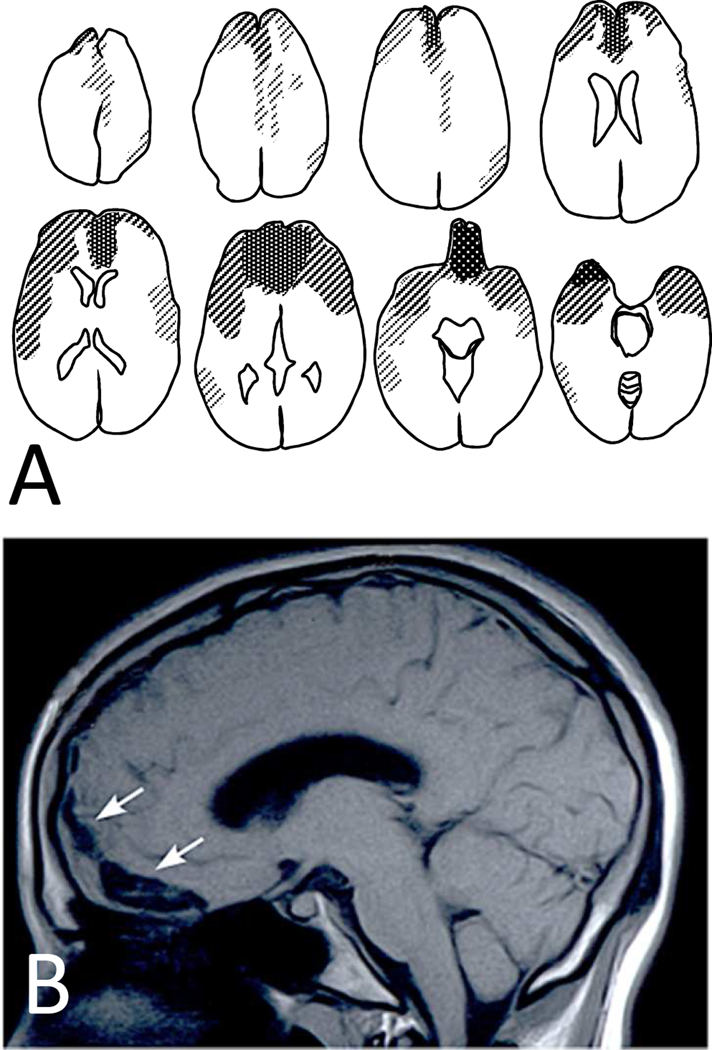
Figure 2.
In brain contusions, concentration of pathology is in orbitofrontal and temporopolar regions. When such cases survive, they often get referred to neuropsychiatric clinics because of chronic and pervasive affective, social, and cognitive changes. Panel A is a compound diagram of brain scans from 28 cases with frontal contusions seen in the Neuropsychiatry Program at Sheppard Pratt. Panel B is a representative case from a 20-year-old patient with orbitofrontal contusion (arrows) resulting from a fall. The patient presented with intact general intelligence but impulsive and inappropriate behaviors causing him to be expelled from college and live a marginal life at home.