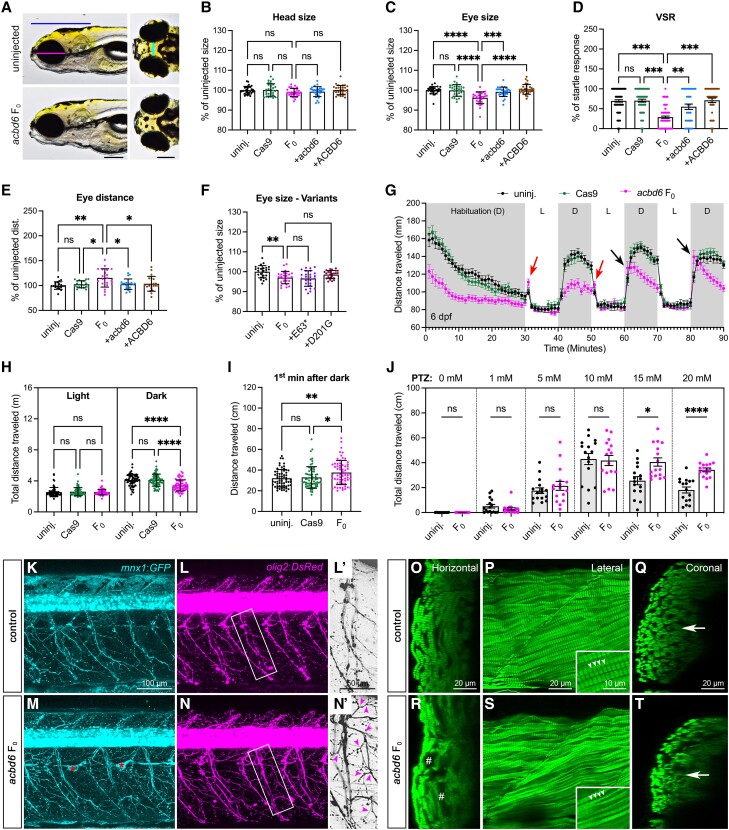
Figure 4.
Zebrafish acbd6 F0 knockouts exhibit increased susceptibility to chemical-induced seizures, excessive motor neuron branching and skeletal muscle degeneration. (A) Representative images of uninjected control and acbd6 F0 larvae at 6 days post-fertilization (dpf). Left: Ventral view, anterior to the left. Right: Dorsal view, anterior to the left. Blue line indicates head size; magenta line indicates eye size; and cyan line indicates eye distance. Scale bar = 0.2 mm. (B and C) Quantification of the head and eye size (n = 30 larvae for each group) of uninjected control (uninj.), acbd6 F0 knockout (F0), F0 + zebrafish wild-type acbd6 mRNA (+acbd6) and F0 + human wild-type ACBD6 mRNA (+ACBD6) as indicated in B. (D) The visual startle response (VSR) analysis after mRNA rescue at 6 dpf. n = 36 larvae for each group. Each symbol represents one larva. The number of responses to five stimuli of each larva was calculated as a percentage of responses. Error bars = mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). (E) Quantification of the eyes distance (n = 20 larvae for each group) as indicated in B. (F) Quantification of the eye size of F0 knockout rescued with mRNA of human p.Glu63Ter (+E63*) or p.Asp201Gly (+D201G) variant. n = 25 larvae for each group. (G) Locomotor activities of zebrafish larvae in light and dark conditions at 6 dpf. n = 64 larvae for each group. The larvae were habituated in the dark for 30 min, followed by three cycles of 10-min periods of light and dark. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM. D = dark period; L = light period. Red arrows indicate increased movement of F0 1 min after light on, and black arrows indicate increased movement 1 min after light off. (H) Average cumulative distance travelled by each larva during three cycles of either light or dark periods in G. Error bars = mean ± standard deviation (SD). (I) The average cumulative distance traveled by each larva during the first minute of the dark period was measured over three cycles, as shown by the black arrow in G. Error bars represent the mean ± SD. (J) The average cumulative distance traveled by the larvae was measured for each group after being treated with different doses of pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) at 5 dpf. n = 16 larvae for each group. (K–N) Confocal images of Tg(mnx1:GFP; olig2:DsRed) larva at 12 dpf are shown, with transgenic larvae injected with slc45a2 sgRNA used as a control and those injected with acbd6 + slc45a2 sgRNAs shown as acbd6 F0. (L' and N') Enlarged images from white boxes are shown in L' and N', with red asterisks indicating autofluorescence from remaining pigment cells. GFP and DsRed are displayed in cyan and magenta, respectively, with magenta arrowheads indicating excess axonal arborizations. The images are presented in a lateral view, with anterior to the left and dorsal to the top. Additional motor neuron phenotypes at 6 and 12 dpf can be found in Supplementary Fig. 13. (O–T) Confocal images of stained skeletal muscle fibers with phalloidin are presented, including images from slc45a2 sgRNA-injected control (O–Q) and acbd6 + slc45a2 sgRNA-injected (R and S) larvae at 12 dpf. Orthogonal views generated from P and S using the Orthogonal views tool in ImageJ are also displayed. #Degenerated muscles. White arrowheads and a white arrow indicate Z-discs and the thickness of the myotube, respectively. Supplementary Fig. 14 provides additional muscle phenotypes at 6 and 12 dpf. In B–D and F, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; E and H–J, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s T3 multiple comparisons test; ns, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.