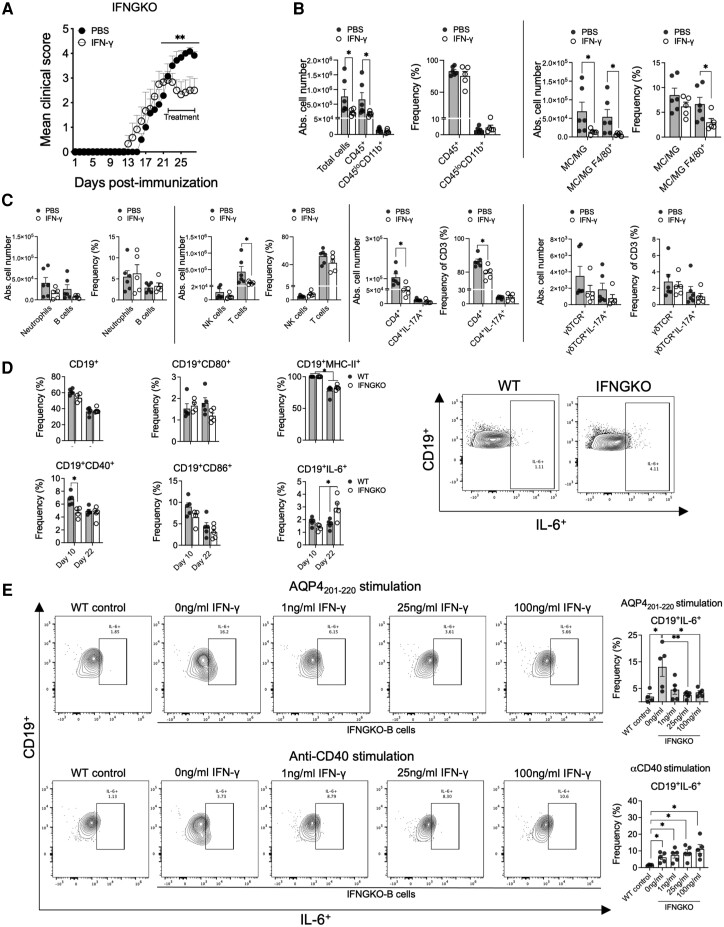
Figure 5.
IFN-γ treatment reduces clinical severity and CNS inflammatory cell infiltration in IFN-γ knockout (IFNGKO) mice with AQP4 201-220 -induced disease. Mean clinical scores of AQP4201-220-immunized IFNGKO mice treated daily with recombinant IFN-γ (open circles, n = 5) or PBS (filled circles, n = 6) starting at the peak of the disease (Day 21) (A). Absolute cell numbers of total CNS mononuclear cells, CD45+ cells and CD45loCD11b+ cells (analysed by flow cytometry) for IFN-γ-treated (open circles) (n = 6) or PBS-treated (filled circles) (n = 5) mice (B). Absolute cell number and frequencies of monocytes/macrophages (MC)/activated microglia (MG;CD45hi), MC/MGF4/80+, Neutrophils Ly6G+, NK (NK1.1+), CD3+, CD4+, CD4+17A+, γδTCR+, γδTCR+IL-17A+ and CD19+ cells were determined by flowcytometry analyses (C). Flow cytometry frequency analysis of expression of activation markers (CD40, CD80, CD86, MHC-II and IL-6) on CD19+ cells at Days 10 and 22 post-immunization (p.i.) in wild-type (WT) (n = 5) and IFNGKO (n = 5) AQP4201-220-immunized mice (D). Pan-B cells purified from spleens of IFNGKO mice stimulated with 40 μg/ml AQP4201-220 peptide or 1 μg/ml of coated anti-CD40 antibody for 72 h, with 0, 1, 25 and 100 ng/ml of IFN-γ. Frequencies of CD19+IL-6+ B cells were determined (E).WT pan-B cells were used as controls. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using the Mann-Whitney test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.