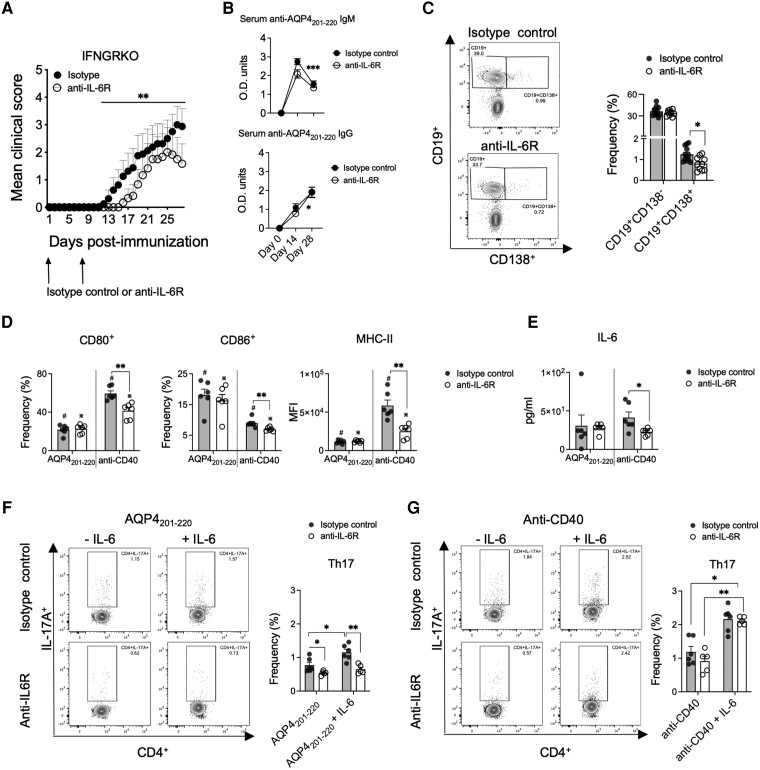
Figure 7.
IL-6 signalling regulates severity of AQP4201–220-induced disease and modulates B-cell activation and induction of Th17 cells. Mean clinical scores of AQP4201–220-immunized IFN-γ-receptor knockout (IFNGRKO) mice treated with two weekly doses of anti-IL-6R (open circles, n = 10) or isotype control antibody (filled circles, n = 13) starting at Day 0 (A). Optical density of total serum anti-AQP4201–220-specific IgM and IgG of mice treated with anti-IL6R (open circles, n = 6) or isotype control (filled circles, n = 8) antibodies were determined by ELISA at Days 0, 14 and 28 post-immunization (p.i.) (B). Flow cytometry frequency analysis of spleen CD19+CD138+ and CD19+CD138− cells at Day 8 p.i. from mice treated with anti-IL6R (open circles, n = 10) and isotype control (filled circles, n = 12) antibodies (C). Flow cytometry frequency analysis of total CD19+ pan-B cells purified at Day 8 p.i. from spleens of anti-IL6R (n = 6)- or isotype control (n = 6)-treated mice stimulated with 40 μg/ml of AQP4201–220 peptide or 1 μg/ml of coated anti-CD40 for 72 h. Frequencies of CD80+ and CD86+ B cells, and MFI of MHC-II (D), as well as supernatant levels of IL-6 (measured by multiplex cytokine assay) (E) were determined. B cells stimulated for 24 h with either AQP4201–220 peptide (F) or anti-CD40 (G) were washed and replated with untouched purified CD4+ T cells from IFNGRKO mice at Day 9 p.i. at 1:1 ratio, with 0 or 10 ng/ml of recombinant IL-6 and cultured for 72 h, and the frequency of Th17 cells was assessed. All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using the Mann–Whitney test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.