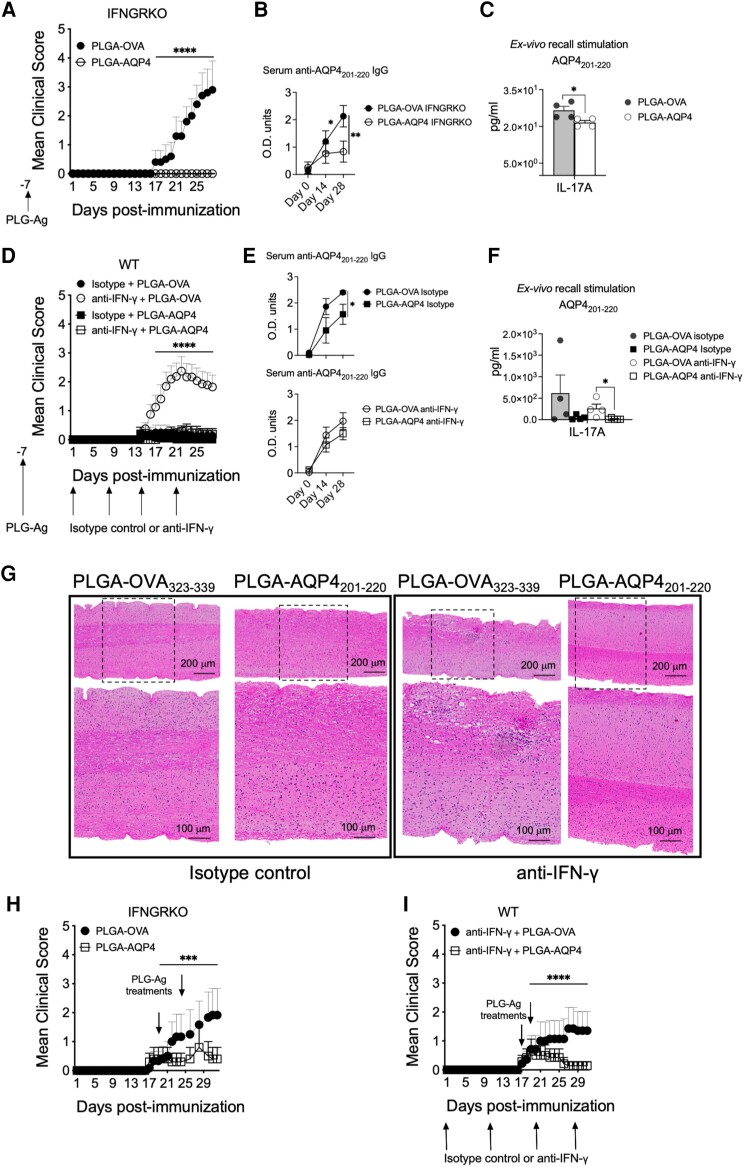
Figure 8.
Immune tolerization by AQP4201–220-coupled PLGA nanoparticles both prevents and ameliorates established AQP4201–220-induced disease. Mean clinical scores of AQP4201–220-immunized IFN-γ-receptor knockout (IFNGRKO) (A and H) and anti-IFN-γ-treated wild-type (WT) (D and I) mice receiving prophylactic intravenous infusion of either PLGA-AQP4201–220 (PLGA-AQP4) or PLGA-OVA323–339 (PLGA-OVA) nanoparticles 7 days prior to AQP4201–220 immunization (Day −7) (A and D), or two therapeutic doses of nanoparticles at disease onset [Days 17–18 and Days 19–22 post-immunization (p.i.)] (H and I). See Supplementary Table 3 for the number of mice in each treatment group. Representative images of haematoxylin and eosin staining of lumbar spinal cord of isotype control- and anti-IFN-γ-treated WT mice that have received a prophylactic treatment with either PLGA-AQP4201–220 or PLGA-OVA323–339 7 days prior to immunization (G). Serum anti-AQP4201–220 IgG was measured by ELISA (B and E) and IL-17A secretion by splenocytes in ex vivo recall experiments quantitated by using multiplex cytokine assays (C and F). All data presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using the Mann–Whitney test. ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. PLGA = poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid).