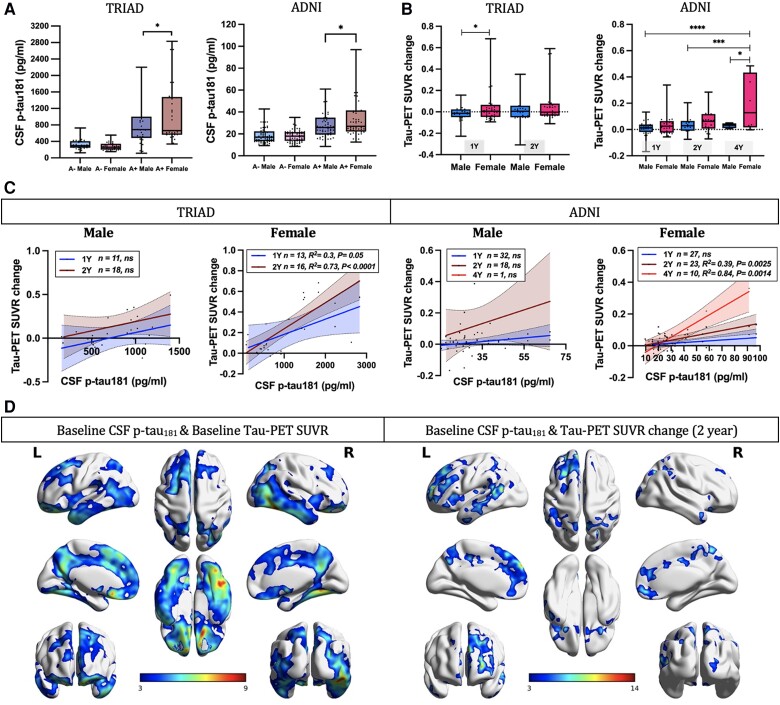
Figure 3.
Tau phosphorylation predicts faster tau accumulation in Aβ+ females. (A) Aβ+ females presented higher CSF p-tau181 concentrations as compared to Aβ+ males in both the TRIAD cohort (P = 0.04, Cohen's d = 0.51) and ADNI cohort (P = 0.027, Cohen's d = 0.41). (B) Aβ+ females also presented faster neurofibrillary tangle (NFT) accumulation compared with Aβ+ males [TRIAD cohort (1-year): P = 0.026, Cohen's d = 0.52; ADNI cohort (4-year): P = 0.049, Cohen's d = 1.14]. (C) In Aβ+ female subjects, baseline CSF p-tau181 concentration was found to associate with the change in tau-PET meta-region of interest (ROI) standardized uptake value ratios (SUVRs) at 1-year (TRIAD: P = 0.05, R2 = 0.3), 2-year (TRIAD: P < 0.0001, R2 = 0.73; ADNI: P = 0.0025, R2 = 0.39) and 4-year follow-up (ADNI: P = 0.0014, R2 = 0.84) assessments. (D) Voxel-based linear regression models demonstrated positive correlations between CSF p-tau181 concentration and baseline tau-PET SUVR as well as longitudinal NFT accumulation in Aβ+ females. The models were corrected for age and APOE ε4 carriage status, and for multiple comparisons using a false discovery rate (FDR) cluster threshold of P < 0.001. ADNI = Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; L = left; R = right; TRIAD = Translational Biomarkers in Aging and Dementia.