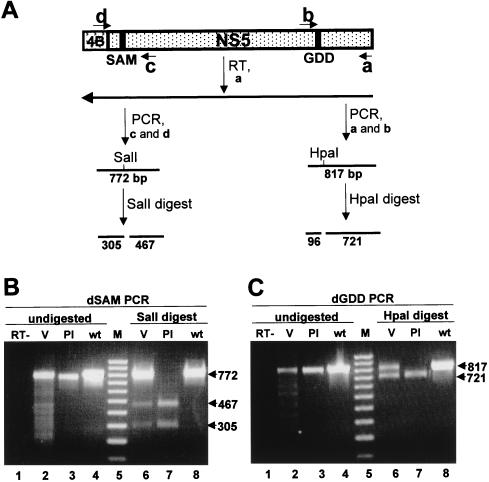
FIG. 7.
Determination of the structure of the defective genomes. (A) Schematic representation of the KUN virus genome in the vicinity of the NS5 gene and the details of the RT-PCR protocol. SAM and GDD represent deleted motifs (Fig. 3). a, b, c, and d represent primers used for RT and PCR and correspond to the published KUN virus plus-sense sequence (9, 14). a, nucleotides 10378 to 10398 (minus sense); b, nucleotides 9576 to 9597 (plus sense); c, nucleotides 8372 to 8400 (minus sense); d, nucleotides 7606 to 7621 (plus sense). Lines marked SalI and HpaI indicate the positions of new sites in the defective genomes introduced into their cDNAs during construction (Fig. 3B). Numbers indicate the predicted sizes of the fragments obtained by PCR amplification and restriction digestion. 4B, NS4B. (B and C) Results of RT-PCR and restriction digest analyses of the RNAs isolated from the culture fluid collected at 7 days after transfection of FLdSAM RNA and at 5 days after transfection of FLdGDD RNA, respectively. The primer for RT was a for both reactions; the primer pairs for PCR were a and b for FLdGDD samples and c and d for FLdSAM samples (see panel A). Lanes 1 in both panels B and C contain PCR products from the parallel control reaction lacking reverse transcriptase (RT−). Lanes 2 contain the PCR products obtained from the RT reactions performed with RNAs from the defective viruses (V) FLdSAM (B) and FLdGDD (C). Lanes 3 contain the PCR products obtained after amplification of the plasmid DNAs (Pl) FLdSAM (B) and FLdGDD (C). Lanes 4 contain the PCR products obtained from the parental FLSDX plasmid DNA with primers specific for SAM (B) and GDD (C). Lanes 6 and 7 contain restriction digests of the corresponding purified PCR fragments shown in lanes 2 to 4 with SalI (B) or HpaI (C) restrictases. Lanes 5 in both panels B and C contain a 100-bp molecular size marker (M) (Progene, Brisbane, Australia). Arrows show the sizes (in thousands) of the undigested and digested DNA fragments. wt, wild type.