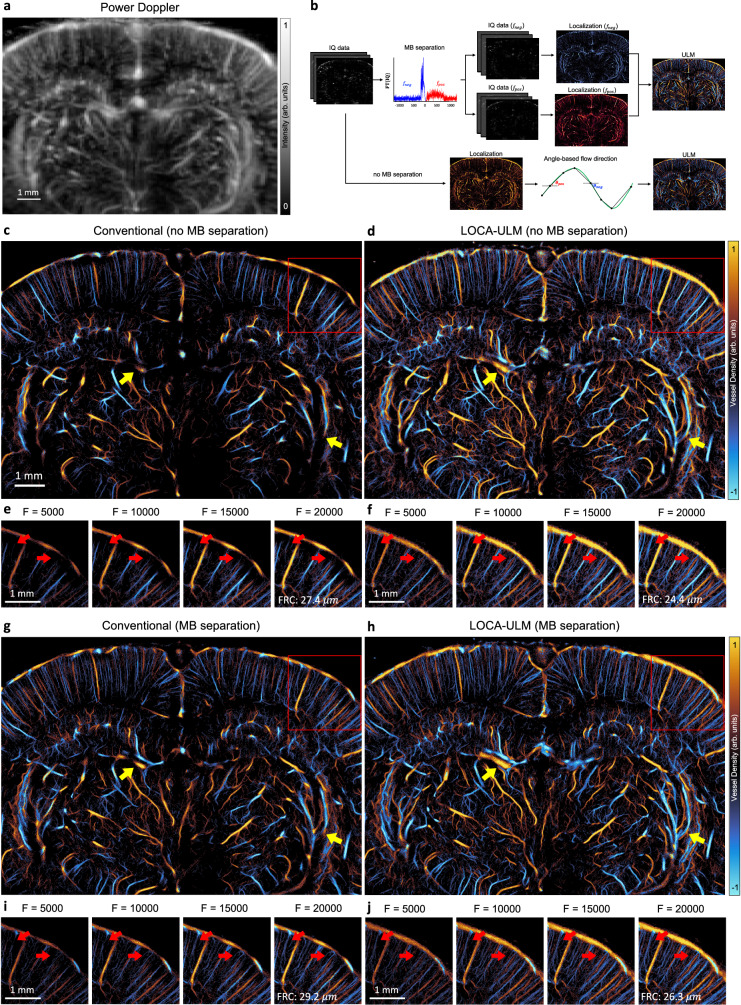
Fig. 3. Comparison of LOCA-ULM and conventional localization to in vivo rat brain ultrasound data.
a Power Doppler image generated by accumulating 2500 frames (a total of 10 s of acquisition, bregma: −4.4 mm) of rat brain ultrasound data. b In vivo rat brain localization workflow. The IQ data after tissue clutter filtering was processed with and without Fourier-based MB separation. For MB separation, the high-concentration MB dataset was divided into subsets of upward and downward flow towards the transducer using a directional filter10. Angle-based flow direction was used for the dataset without MB separation. For each dataset, MB locations was determined by performing normalized cross-correlation with an empirically determined PSF function (i.e., conventional localization) or LOCA-ULM. The uTrack algorithm was used to pair the localized MB centers and estimate their trajectories. c–j Each ULM directional flow maps were generated by accumulating 20,000 frames (a total of 80 s of acquisition), c, d without MB separation and g,h with MB separation. e, f, i, j Improvement of vessel structures with respect to the increasing number of frames is displayed on the bottom, shown for the area marked with a red rectangle. n = 1 experiment. F indicates the number of frames used for ULM reconstruction, and FRC indicates Fourier ring correlation.