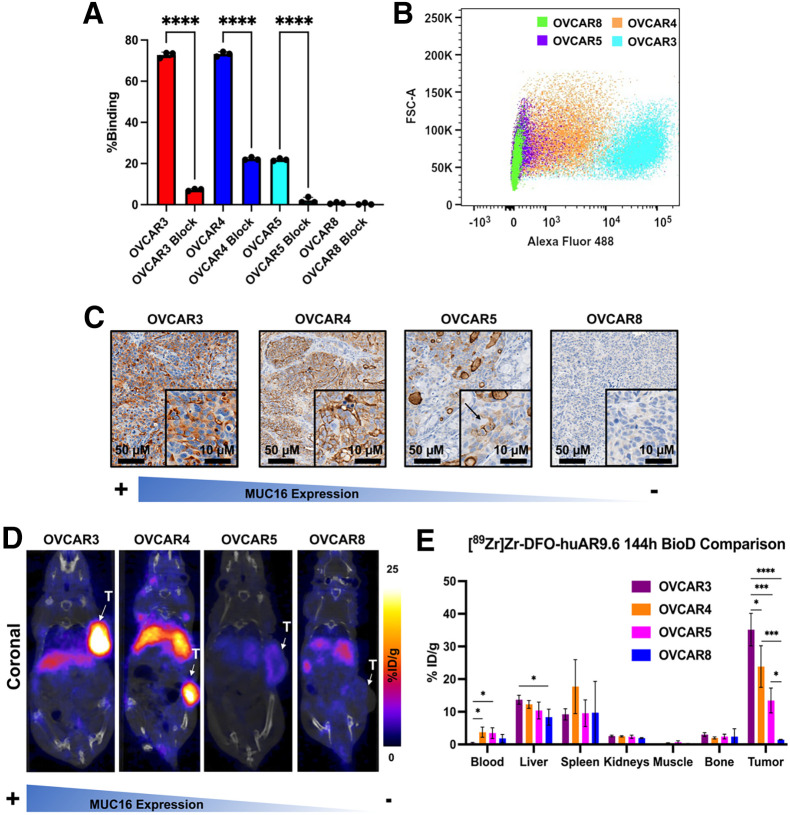
FIGURE 1.
huAR9.6 can differentiate between OC cells with high and low MUC16 expression in vitro and in vivo. (A) Radioligand cell-binding assay with [89Zr]Zr-DFO-huAR9.6 in cell lines with varying levels of MUC16 expression. Binding was significantly reduced with administration of 1,000-fold excess blocking dose of nonlabeled huAR9.6. (B) In vitro validation of huAR9.6-AF488 binding in OC cells via flow cytometry. (C) huAR9.6 immunohistochemical staining images of harvested OVCAR3, OVCAR4, OVCAR5, and OVCAR8 subcutaneous tumors. Arrow indicates MUC16 expression on surface of OVCAR5 cells. (D) Female nude mice containing subcutaneous tumors that were injected with 7.4–9.25 MBq (20–25 μg) of [89Zr]Zr-DFO-huAR9.6 followed by PET imaging. (E) Terminal biodistributions at 144 h after injection. n = 3 for OVCAR4 and OVCAR8; n = 4 for OVCAR3 and OVCAR5. *P ≤ 0.05. ***P ≤ 0.001. ****P ≤ 0.0001. %ID = percentage injected dose; FSC-A = forward scatter area; T = tumor.