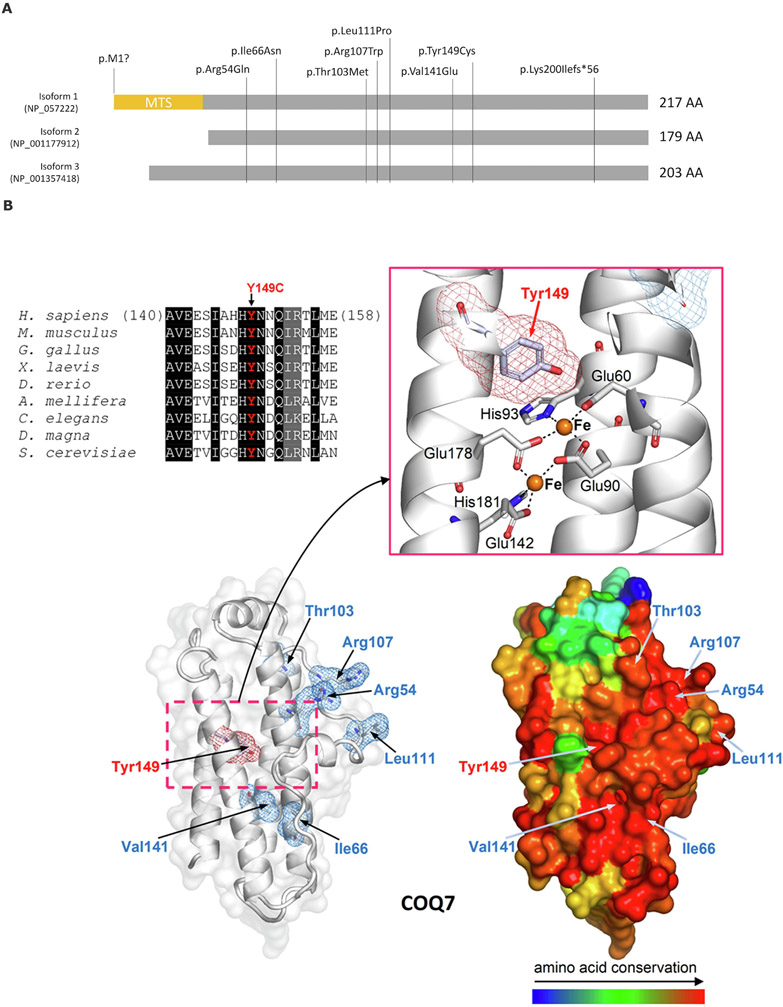
Figure 1. COQ7 protein structure and known disease-associated variants.
(A) Three main isoforms of COQ7 proteins and all known disease-associated variants reported. MTS-mitochondrial targeting sequence (adapted from Jacquier, et al[23]). (B) Multiple sequence alignment highlights the conservation of Tyr149. Columns with identical and similar residues are shadowed, respectively, in black and gray. The homology model of 5-demethoxyubiquinone hydroxylase (based on PDB structure 2VZB; see Materials and Methods for details) is shown with the site of Tyr149Cys replacement (Tyr149 is highlighted by red meshes) and of the previously reported variants p.Arg54Gln, p.Arg107Trp, p.Leu111Pro, and p.Val141Glu (highlighted by blue meshes). On the left, the COQ7 model is presented showing the protein structure as white ribbons and transparent protein surface (the zoomed view details Tyr149, the two active iron ions, represented by orange spheres, and the metal-coordinating residues). On the right, the same model is represented as protein surface colored according to amino acid conservation (as inferred from the multiple sequence alignment of homologous proteins from the following organisms/UniProt entries: H. sapiens, Q99807; M. musculus, P97478; G. gallus, A0A1D5NTT1; X. laevis, Q640V8; D. rerio, F1QW05; A. mellifera, Q6J4P7; C. elegans, P48376; D. magna, A0A0P6DRG9; S. cerevisiae, P41735).