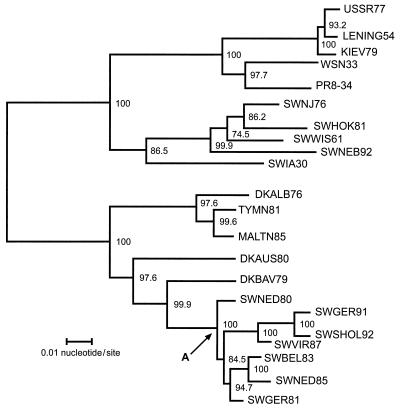
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic tree of influenza A virus H1 HA genes. Nucleotide residues 1 to 1731 of each H1 HA were analyzed by the neighbor-joining method (34). Horizontal distances are proportional to the minimum number of nucleotide differences required to join nodes and H1 HA sequences. Vertical lines are for spacing branches and labels. Bootstrap values (1,000 replications) are presented for each node. The node shown by the arrow at A indicates the hypothetical introductory virus in pigs that originated from birds. The HA nucleotide sequences represent USSR77 (A/USSR/90/77), KIEV79 (A/Kiev/59/79), SWHOK81 (A/swine/Hokkaido/2/81), SWWIS61 (A/swine/Wisconsin/1/61), SWIW30 (A/swine/Iowa/15/30), DKALB (A/duck/Alberta/35/76), TYMN81 (A/turkey/Minnesota/1661/81), MALTN85 (A/mallard/Tennessee/11464/85), DKAUS80 (A/duck/Australia/749/80), DKBAV (A/duck/Bavaria/1/77), SWNED80 (A/swine/Netherlands/3/80), SWGER91 (A/swine/Germany/8533/91), SWSHOL (A/swine/Schleswig-Holstein/1/92), SWVIR (A/swine/Italy-Vir/671/87), SWBEL83 (A/swine/Belgium/1/83), SWNED85 (A/swine/Netherlands/12/85), and SWGER81 (A/swine/Germany/2/81) from this study; LENING54 (A/Leningrad/1/54), reported by Beklemishev et al. (2); WSN33 (A/WSN/33), reported by Hiti et al. (19); PR8-34 (A/Puerto Rico/8/34), reported by Winter et al. (41); SWNJ76 (A/swine/New Jersey/11/76), reported by Both et al. (5); and SWNEB92 (A/swine/Nebraska/1/92) reported by Olsen et al. (30).