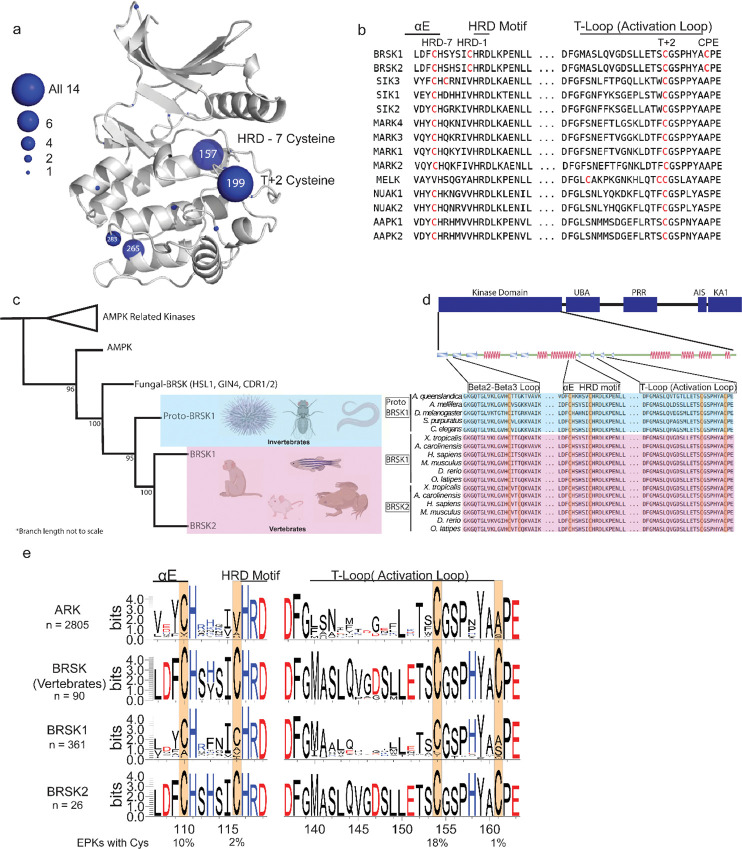
Figure 3:
Cysteine pairs are highly conserved within the activation segments of BRSKs. (a) Mapping of Cys residues (spheres) in the kinase domains of human ARK family members. Numbers represent the corresponding amino acid position in PKA. Sphere size is proportional to the number of ARKs that contain a Cys at a specific site. (b) Activation segment sequence alignment of the 14 human ARKs. (c) Phylogenetic analysis showing divergence and grouping of BRSKs subfamilies in different taxonomic groups. Bootstrap values are included for each clade. (d) Sequence alignment of the kinase domains of invertebrate and vertebrate BRSKs. (e) Analysis of relative amino acid conservation in ARKs and BRSKs, centered on the HRD containing catalytic loop, and the T-loop (between the DFG and APE motifs). Data is presented as HMM (hidden Markov models) Sequence Logos. The % of ePKs that possess a specific Cys is shown at the bottom.