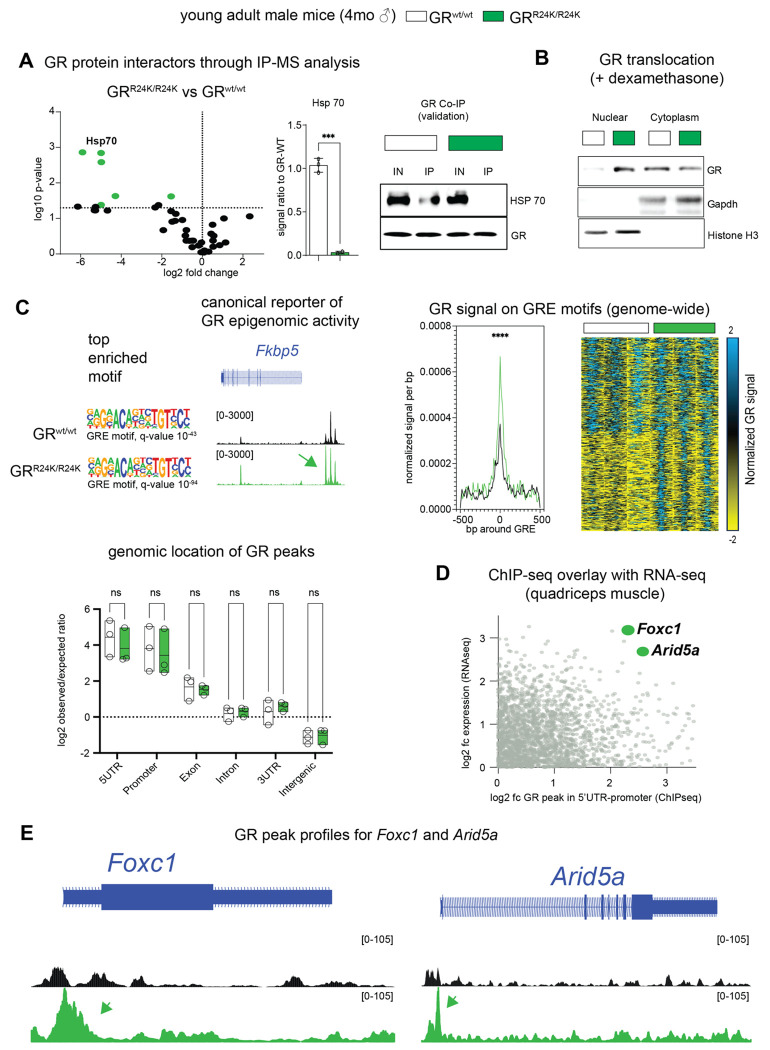
Figure2. The mutant GR shows increased transactivation activity in muscle.
(A). IP-MS analysis of wild type and mutant muscles revealed decreased binding of the mutant GR for Hsp70, confirmed through CoIP. (B). Upon glucocorticoid stimulation in vivo, the muscle mutant GR showed increased nuclear translocation compared to WT GR. (C). Muscle ChIP-seq revealed increased epigenomic GR activity with maintained peak enrichment in 5’UTR-promoter regions for the mutant GR. (D). ChIP-seq overlay with RNA-seq revealed Foxc1 and Arid5a as top transactivation targets of the mutant GR. (E) GR peak profiles showed gain of mutant GR signal on proximal promoter regions for both genes. N=3–5/group; Welch’s t-test (A, histogram); 2w ANOVA + Sidak (C); *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001; ****, P<0.0001.