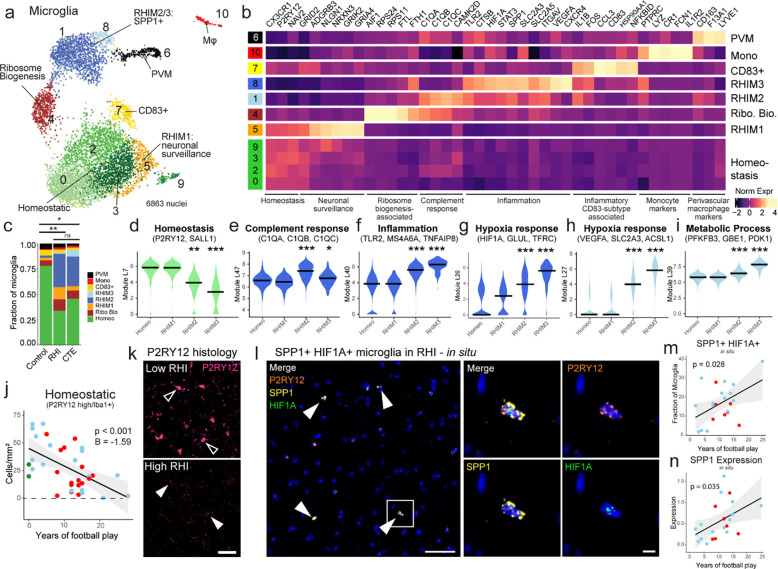
Figure 2. RHI Exposure induces distinct microglial phenotypes.
a. UMAP of microglia colored by 11 Seurat clusters determined by unsupervised clustering. b. Heatmap of selected cluster DEGs annotated by function. c. Proportion of microglial subtypes per pathological group. Statistical analysis was performed using a chi-squared test. d-i. Violin plots representing the expression of Celda gene modules. Color represents the cellular subtype most associated with the module. Black line represents median statistic from ggsignif. Statistical analysis performed by linear mixed modeling correcting for patient-specific effects. *, p <0.05, **, p <0.01, ***, p.<0.001. j. Scatter plot depicting the density of immunohistochemically labeled homeostatic microglia (P2RY12 high /Iba1+) in the grey matter sulcus compared to years of football play, colored by pathological group identity. Statistical analysis performed by linear regression with age as a covariate. k. Representative image of P2RY12 immunofluorescent labeling (pink) in a low RHI and high RHI individual. Open arrows depict high P2RY12-expressing cells. Solid arrows depict low P2RY12-expressing cells. Scale bar 50μm. l. Representative image depicting in situ hybridization of SPP1+ (yellow)/HIF1A+ (green)/P2RY12+ (orange) microglia in an RHI-exposed individual. Solid arrows indicate triple-positive cells. White box indicates inset displayed on the right. Left scale bar 50μm, right scale bar 5μm. m, n. Scatter plot depicting SPP1+ HIF1A+ microglial fraction and microglial SPP1 expression in the grey matter sulcus compared to years of football play. Colored by pathological group status. Statistical analysis performed by linear regression.