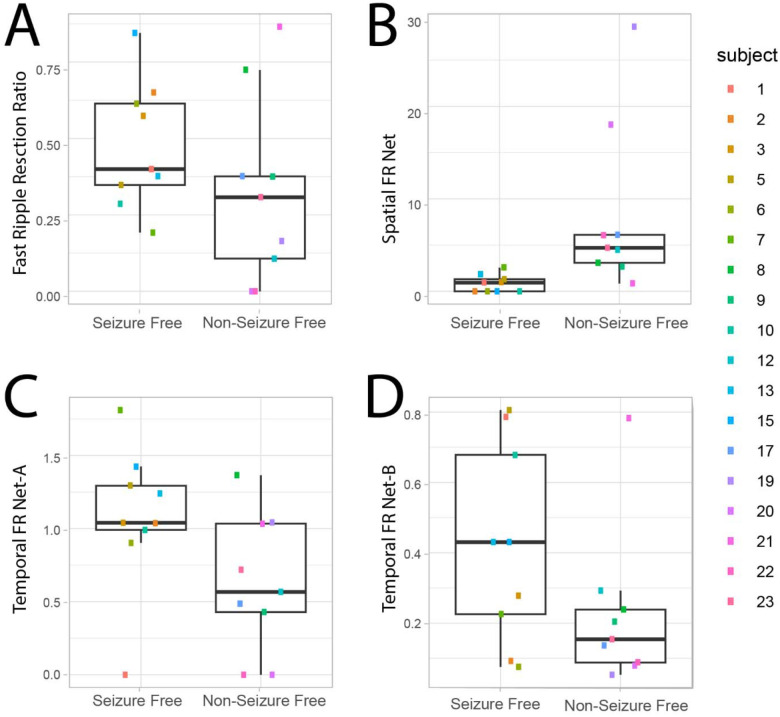
Figure 3: Four fast ripple (FR) factors used for training and testing a support vector machine (SVM) to label seizure free patients show differences in seizure free patients.
The four factors used fast ripple (FR) on oscillation >350 Hz and all FR on spikes (200–600 Hz). (A-D) Box and scatter plots of the four metrics between seizure free and non-seizure free outcome. (A) The FR RR trended higher in seizure free patients (Kruskal-Walis Chi-sq=2.13, p=0.15). The spatial FR net metric was significantly higher in the non-seizure free patients compared with seizure free patients (Kruskal-Wallis Chi-Sq = 9.92, p=0.002, n=18). The temporal FR net-A metric trended (C) higher in the seizure free patients (Kruskal-Wallis Chi-Sq = 3.29, p=0.07, n=18). The temporal FR net-B metric also trended higher in the seizure free patients (Kruskal-Wallis Chi-Sq = 2.67, p=0.10, n=18). When all four of these metrics (FR RR, Spatial FR Net, Temporal FR Net-A, B) were used as factors to train a support vector machine to label seizure free patients, the SVM exhibited a 78% accuracy with leave one out cross-validation. Patient identification numbers labeled as in Table 1.