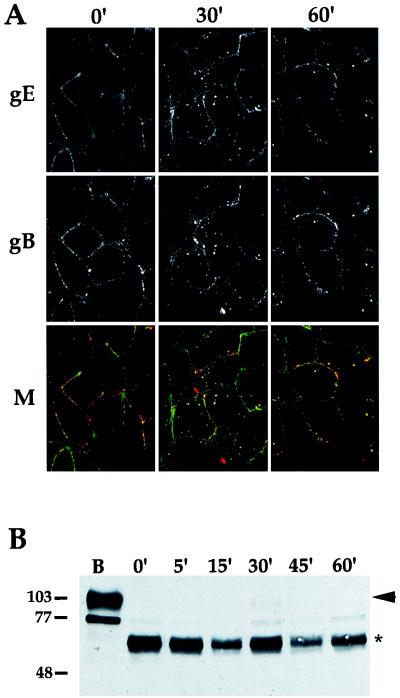
FIG. 5.
Internalization of gB and gC. (A) PK15 cells were infected with PRV Be (wild type) at an MOI of 10 for 4 h. An indirect immunofluorescence endocytosis assay was then performed as described in the legend for Fig. 2, using the monoclonal antibody (1/14) that recognized gE when complexed with gI (row gE) and a polyclonal goat antiserum (284) against gB (row gB). A merge of the two fields is shown in row M. The gE-gI complex is shown in green, and gB is shown in red. (B) Endocytosis of gC was determined by biotinylation-trypsin digestion as described in the legend to Fig. 4. The cells were either lysed immediately (lane B), treated with trypsin immediately (0 min), or shifted to 37°C for the times indicated (5 to 60 min) prior to trypsin treatment. Western blot analysis was performed with polyclonal goat antiserum to gC. Full-length gC protein is marked with an arrowhead, while the protease-resistant fragment is indicated by an asterisk. A biotinylated precursor form of gC is below the 77-kDa mark. Apparent molecular mass markers are indicated on the left in kilodaltons.